| cocci |
| spherical shaped bacteria |
| bacillus |
| clylindrical or rod shaped bacteria |
| total magnification of all lenses on a microscope |
|
ocular lens: 10x scanning lens: 4x low power lens: 10x high power lens (dry): 40x oil emersion lens: 100x |
| total magnification |
| the amount a specimen is magnified through the objective & ocular lenses combined |
| microscope parts |
| ocular lens, arm, base, light source, stage, stage clips, fine & course adjustment knobs, condensor, iris, diaphragm, nose piece, scanning lens, low power objective, high power objective, and oil emersion lens |
| working distance |
| the amount of space between the objective and the specimen when the latter is in focus |
| parfocal |
| when one objective can be exchanged for another with only minor adjustments |
| wavelength of light |
| visable light that aids in resolving power |
| numerical aperture of a lens |
|
ability of a lens to gather light
NA = i sin 0 |
| magnification |
| making an object appear larger from use of one or more lenses |
| resolution/resolving power |
| ability of a lens or microscope to distinguish between closely adjacent points |
|
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Yeast |

|
| Description of the Kingdom Algae |
|
photosynthetic eukaryotes w/ membrane bound nucleus & chlroplast oxygen generating primary producers |
|
Spirulina
cyanobacteria |
|
microcystis
cyanobacteria |
|
Anabaena
cyanobacteria |
|
oscillatoria
cyanobacteria |

|
|
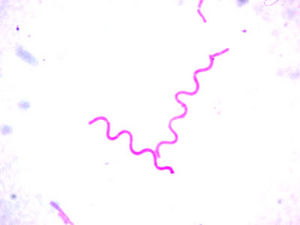
Spirillum sp.
bacteria |
|
|
Streptococcus pyogenes
bacteria |

|
|
Proteus vulgaris
bacteria |

|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
bacteria |

|
| spirilla |
|
spherical shaped
1/2 moons, loosely wound, or tightly wound |
|
Bacillus subtilis
bacteria |

|
| description of Kingdom Protozoa |
|
eukaryotic grouped based on motility primary consumers |
|
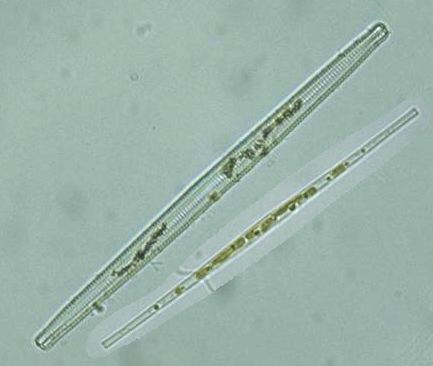
Synedra
|
|
diatom
Chrysophyta |
| Synedra |
|
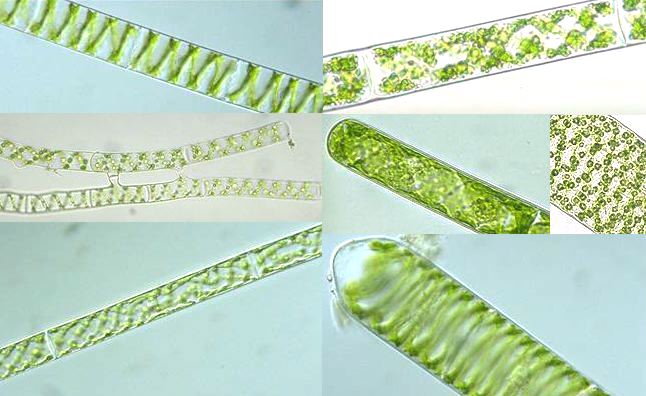
| Spirogyra |
|
filamentous algae
Chlorophyta |
| Spirogyra |
|
| Chlamydomonas |
|
unicellular green algae
(Chlrophyta-Mastigophoa) |
| Chlamydomonas |

|
| Euglena |
| Euglenophyta-Mastigophora |
| Euglena |

|
| Giardia lamblia |
| Mastigophora |
| Giardia lamblia |

|
| hypha |
| growth form of most fungi is a tubular cell |
| septae |
| cross walls located inside of the hypha structure |
| coenocytic |
| condition of free movement |
| myecelium |
| many branched hypha |
|
oogonia
(specifically in Saprolegenia) |
| immature ovum |
| Description of Basidiomycetes |
| when sexual spores are formed inside a basidium; includes mushrooms and toad stools |
| Description of ascomycetes |
| spores are formed inside a structure called an ascus |
| Lower Fungi description |
| bread & water mold, where enclosed sexual spores of all other types |
| Deuteromycetes |
| no sexual stage is observed |
| disease of Aspergillus |
| Aspergillosis...causes allergic respiratory symptoms |
| disease of Rhizopus |
| causes bread mold |
| disease of Candida |
| causes yeast infections in women & men |
| Name mold that created first antibiotic |
| Penicillium |
| Penicillium |

|
| Aspergillus |

|
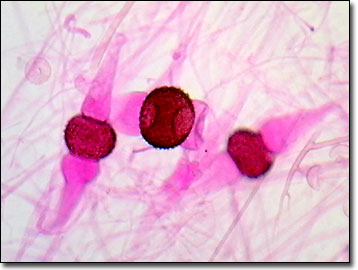
| Rhizopus |

|
| Rhizopus conjugation |
|
| Budding yeast |

|
| Saprolegnia |

|
| Candida albicans |

|
| description of Phylum Platyhelminthes |
|
includes Trematode & Cestode commonly called flukes (one animal consisting of both male & female) require alternate host
|
| description of Phylum Nematoda |
|
roundworms
|
| schistosoma mansoni male & female |
|
|
| schistosoma mansoni cercariae |

|
| schistosoma mansoni miracidium |

|
| trematoda |

|
| nemotoda |
|
|
| cestoda - proglottis |

|
| cestoda - cysticercus |

|
| cestoda - scolex |
|
|
| nemotoda - scolex |
|
|
| nematoda |

|
| nematoda |

|
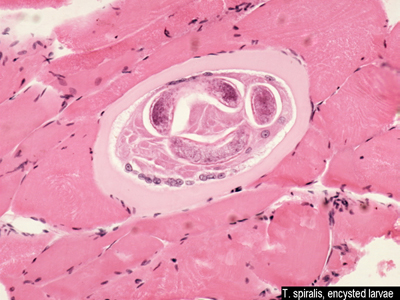
| nematoda - larvae encysted |

|
| nematoda - migratory larvae |
|
| symptoms of hookworm |
|
common in africa chronic anemia due to loss of blood dermatitis removal of worms from throat |
| symptoms of pinworm |
|
anal area irritation noticed because of intense scratching tiredness & irritability |