|
Scalpel Handle #3 -used in sm animal - uses blades 10, 11, 12, 15 Scalpel handle #4 - used in lg animal -uses blades 20, 21, 22 -blade 20 is most common |
|
Bard Parker |
|
-Scalpel handle holds the scalpel blades for easy use -Best instrument for incising tissues with minimal trauma -Variety of disposable blades are designed to fit several different handles |
| Bard Parker |

|
| Brown-Adson Thumb Forcep |
|
-Special tissue forceps designed to hold and easily release tissue -Having spring action; jaws are opposed by compressing 2 metal handles together -Available in a variety of different sizes -Several jaw surfaces are available and are designed for use with various tissues |
| Thumb Forceps |
|
|
| Adson Thumb Forcep |
|
|
| Rat Tooth Thumb Forcep |
 |
| DeBakey Thumb Forceps |
|
-Have delicate intermeshing teeth that provide a good atraumatic grasp of delicate tissue - commonly used for disection |
| Adson Thumb Forcep |
|
-Have multiple intermeshing teeth with a broad tip, providing good tissue and needle handling - Commonly used during suturing/wound closing |
| Brown-Adson Thumb Forcep |
| - Have large interdigiting teeth and are primarily used for skin or fascia |
| Rat Tooth Thumb Forcep |
| -Have long, narrow jaws with multiple delicate sets of teeth that are especially good for vascular surgery |
| DeBakey Thumb Forcep |
| -Have a broad curved surface good for needle holding but are traumatic when used to grasp/hold tissue |
| Russian Thumb Forcep |

|
| Russian Thumb Forcep |

|
| Dressing Thumb Forcep |
|
- DO NOT HAVE TEETH and are used for applying and removing dressings (bandages) -Are NOT designed to grasp tissue because the surgeon must squeeze hard and crush the tissue in order to grasp it |
| Dressing Thumb Forcep |

|
| Mayo Hegar Needleholder |

|
| Olsen Hegar Needleholder |
|
-Built in scissors -May accidently cut the suture "Oops, I cut the suture" |
| Olsen Hegar Needleholder |

|
| "Dinky" Derf Needleholder |
|
- Used primarily for opthalmic procedures - "Dinky" smaller than other needleholders (used on delicate eyes) - Usually 4- 4 1/2 inches in length |
| "Dinky" Derf Needleholder |
|
- Designed for holding curved suture needles/tying suture during suturing - Size and design vary depending on their intended use - Improper use of needle holders damages the jaws and the box lock and ratchet - Do not use for anything other than the intended purpose |
| Needleholders |

|
| Allis Tissue Forceps |
|
- Securely grasps tissue but also crushes it - Should only be used on tissue that is going to be removed - Commonly Used
|
| Allis Tissue Forceps |

|
| Babcock Tissue Forceps |

|
| Doyen Intestional Tissue Forcep |
|
- More delicate tissue instrument - Used to occlude and hold the intestion
- Disadvantages- less secure hold on tissues |
| Doyen Intestional Tissue Forcep |
|
- Locking instruments that clamp tissues - Different teeth patterns allow them to grip various types of tissue w/o slipping |
| Tissue Forceps |
|
- Shaped similarly to Allis, but are less traumatic - Have smoother grasping surface - Less tip compression - NOT as common |
| Babcock Tissue Forcep |

|
| Backhaus Towel Clamp |
|
- Used to attach towels and drapes to the patient - Have pointed *sharp* tips that curve and join like ice tongs |
| Backhaus Towel Clamp |

|
| Roeder Towel Clamp |
|
- Has a metal bead or ball stop attached to the jaws that prevents deep tissue penetration - Prevents towel from slipping toward the box lock |
| Roeder Towel Clamp |

|
| Halsted Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps |
|
- small and designed to occlude small vessels - Tips of the forceps should be used to grasp only as much tissue as necessary - Serrations go all the way down the tip of the instrument
|
| Halsted Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps |
|
- Tissue forceps used to stop bleeding/occlude blood supple to tissue by crushing blood vessels or the tissue itself - Available in many different sizes and may be straight or curved - Have grooves on the inside surface of the jaws to better grasp the tissue |
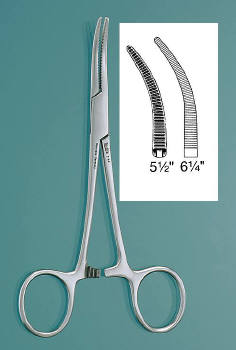
| Hemostatic Forceps |
|
| Crile Hemostatic Forceps |
|
- Larger than a mosquito forcep - Used on larger vessels - Transversely grooved the entire length of the jaw |
| Crile Hemostatic Forcep |

|
| Kelly Forceps |
|
- larger than a mosquito forcep - used on larger vessels - Transversely grooved only on the distal half of the jaw |
| Kelly Hemostatic Forceps |

|
| Rochester-Pean Forceps |
|
- Large - Transversely grooved forceps - Used to clamp tissue in bundles and large vessels |
| Rochester-Pean Forceps |

|
| Rochester-Oshner Forceps |
|
- Similar to Rochester Pean forceps - Have interdigiting teeth at the tips that aid in grasping tissue - Used in orthopedic or large animal surgery |
| Rochester-Oshner Forceps |

|
| Rochester Carmalt Forceps |
|
- Large crushing forceps with longitudinal grooves on the jaw - Cross groove at the tip to provide more traction - used for clamping across tissue containing vessels - Commonly used to crush the vessels of the ovarian pedicle during OVH |
| Rochester Carmalt Forceps |
|
Blunt/Sharp |
| Operating scissors |
|
Sharp/Sharp |
| Operating Scissors |
|
Blunt/Blunt |
| Operating Scissors |
|
- To cut tissue, suture, wire, or bandage material
|
| Scissors |
|
- Often used to cut drape material - Used for dissecting tissue
-Vary by blades:Straight or curved - Vary by points: Blunt/Blunt, Blunt/Sharp, Sharp/Sharp - Cutting edge of the blade: Plain or serrated |
| Operating Scissors |

|
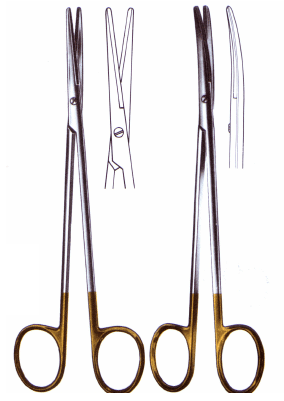
| Mayo Dissection Scissors |
|
- Heavy scissors used for cutting through tissue such as heavy connective tissue - Blades may be curved or straight - "Sturdier" than Metzenbaum considerably longer than operating scissors |
| Mayo Dissecting Scissors |
|
| Metzenbaum Dissecting Scissors |
|
- Fine scissors used for cutting delicate tissue such as fat or thin muscle - Preferred most for soft tissue dissection - NEVER use to cut suture- will dull edges - Very delicate scissors, much "skinnier" than Mayo |
| Metzenbaum Dissecting Scissors |

|
| Littauer Suture Removal Scissors |
| - Used to cut/remove all sutures except wire sutures |
| Littauer Suture Removal Scissors |

|
| Wire Cutting Scissors |
| - Used to cut wire, including wire sutures |
| Wire Cutting Scissors |

|
| Lister Bandage Scissors |
|
- Used to cut bandage material - One blade has a blunt end to facilitate sliding under a bandage w/o cutting the skin |
| Lister Bandage Scissors |

|
| Army-Navy Retractor |
|
- Double ended retractor commonly used to retract skin, fat or muscle - Smooth blades on both sides |
| Army-Navy Retractor |

|
| Senn Retractor |
| - Same as Army-Navy except has one smooth blade and one blade with 3 sharp or blunt prongs |
| Senn Retractor |

|
| Malleable Retractor |
| - Made of thin metal that is easily bent to a desired shape commonly used to retract abdominal organs |
| Malleable Retractor |
|
- Retractors rather than hands should be used in surgery to retract tissues and provide good visibility of the surgical site - Properly placed, they do not interfere with the surgery - 2 Types:Handheld- sterile assistant needed to maintain tissue position and tension Self-Retaining-Maintained in the desired position by some a locking mechanism on the retractor handle -Keeps assistant hands free |
| Retractors |

|
| Snook Ovariohysterectomy Hook |
|
- AKA: Spay Hook - AKA: Snook Hook - Used to expose the uterine horn during an OVH |
| Snook Ovariohysterectomy Hook |

|
| Hohmann Retractor |
|
- Consists of a single blade and a handle that are used to lever tissues out of the way - Used almost exclusively in orthopedics esp. Joint sx |
| Hohmann Retractor |
_lrg.jpg)
|
| Balfour Retractor |
|
- 2 wire-like blades are used to distract the abdominal incision - Solid spoon-like blade is hooked into the sternum to distract caudally |
| Balfour Retractor |

|
| Finochietto Rib Spreader |
|
- Spreads ribs - Ratcheted part is positioned at the dorsal aspect of the thoracic incision |
| Finochietto Rib Spreader |

|
| Gelpi Retractor |
|
- Commonly used for muscle retraction - especially in orthopedic and neurologic sx - More tissue trauma - Very sharp points |
| Gelpi Retractor |

|
| Weitlaner Retractor |
|
- Commonly used for muscle retraction - Especially in orthopedic and neurologic sx - More tissue trauma |
| Weitlaner Retractor |

|
| Rongeur Tip |

|
| Single-Action Rongeur |

|
| Double Action Rongeur |

|
| Kerrison Rongeur |
|
- Have sharp cupped tips that are used to cut small pieces of dense tissue such as bone, cartilage, or fibrous tissue
|
| Rongeur |
|
- Have a smooth cutting action and are mechanically stronger than a single-action rongeur - Larger, preferred for removing lg amts of dense tissue |
| Double-Action Rongeur |
|
- More commonly used in confined areas - ex. removing bone to perform spinal sx |
| Single-Action Rongeur |
|
- Gun shaped appearance - Useful for spinal sx |
| Kerrison Rongeur |

|
| Wire Cutter |

|
| Bone Cutter |
|
- Used to cut bone, NOT wire - look similar to a rongeur but has paired chisel like tips (finer jaws) - DO NOT confuse with wire cutter |
| Bone Cutting Forceps |
|
- Used to cut wire, NOT bone - look similar to a bone cutting forcep but has scissor like tips |
| Wire Cutter |
|
- Designed to hold bone fragments in alignment while orthopedic implants are applied - most are self-retaining |
| Bone Holding Forceps |
|
- Has a ratcheted handle that allows it to be clamped securely on the bone - More common |
| Kern Bone Holding Forcep |
|
- AKA: Speed locks - has a nut that tightens against one handle to squeeze the handles together |
| Self-Retaining Bone Holding Forceps |

|
| Kern Bone Holding Forceps |

|
|
Self-Retaining Bone Holding Forceps AKA: Speed Lock |

|
| Bone Curette |
|
- Used to scrape hard tissue such as bone/cartilage - Have a sm. cuplike structure at one or both ends of a handle - cup has sharp cutting edge available in many sizes - Common to retrieve cancellous bone from the meduallary cavity for use as a bone graft during fracture repair |
| Bone Curette |
|
- Used to pry periosteum or muscle from the bone surface - Have a bladelike structure at 1 or both ends of a handle - Blades have sharp or blunt edges and are available in various sizes |
| Periosteal Elevators |

|
| Periosteal Elevators |
| - Used to cut bone by pounding the flared end of the handle with a mallet |
| Osteotomes and Chisels |
| - Cutting edge is tapered on both sides |
| Osteotome |
| - Cutting edge is tapered only on one side |
| Chisel |
|
- Used to cut bone by placing the wire around the bone and drawing it back and forth in a sawing fashion - T-shaped handles hook onto the wire to give the surgeon a firm grasp of the wire |
| Gigli Wire and Handle |
| - T-shaped tubular instrument with a cylindrical cutting blade used to remove a core of bone for biopsy |
| Trephine |

|
| Osteotome |
|
|
| Mallet and Chisel |

|
| Gigli Wire and Handle |

|
| Trephine |
|
- Commonly used in orthopedic/neurologic surgery - Electric, battery powered, powered by nitrogen gas supplied viz a sterile hose |
| Power Equipment |

|
| Makita drill-battery powered |

|
| 3-M Mini Driver |

|
| ASIF drill |

|
| Hall Air Drill |
|
- Varying in diameter -Length and type of points-2 main types
|
| Bone Pins |
|
- AKA: IM pins - smooth, stainless steel pins ranging in diameter from 1/16 to 1/4 inch - 3 different types available: Chisel, Trocar, Threaded trocar |
| Steinmann Pins |
|
- AKA: K-wires - smaller than IM pins - can be used to pin sm bone fragments - Available sizes are .035, .045, .062 inches |
| Kirschner Wires |
| - Manual "drill" used to place IM pins/K-wires |
| Jacobs Hand Chuck and Key |
|
- Similar to IM pins but have preplaced holes through the pin that allow screw placement - Have more rigid fixation than IM pins |
| Interlocking Nails |
|
- Stainless steel wire supplied on spools - Common sizes in small animal sx are 22 guage, 20 gauge, and 18 gauge - Most commonly applied in a cerclage fashion by encircling the bone/bone fragments and twisting the ends in a "twist tie" manner - Often used for fracture repair in combo with pins/bone plates |
| Orthopedic Wire |
|
- Used to twist wire - NEEDLEHOLDERS SHOULD NOT BE USED |
| Wire Twister |
| - Used as a means of stabilizing fractures using pins placed through the skin and bone |
| External Fixators |
|
- Used alone or in conjunction with bone plates or interlocking nails for fracture repair - 2 types |
| Bone Screws |
| - Fully threaded, narrow threads, used for dense bones |
| Cortical Screws |
| - Full or partial threads that are wider to better grip softer cancellous bone |
| Cancellous Screws |
|
- Used in fracture repair by bending to match the curve of the bone and fastening to it with bone screws - Requires much instrumentation for placement - More complex than other types of fixation - More stable in most cases |
| Bone Plates |
 
|
| Steinmann Pins and Kirschner Wire |
 |
| Wire Twister and Wire Cutter |

|
| Various Bone Screws |

|
| Various Bone Plating Tools |

|
| Various Bone Plates |

|
| External Fixator |
|
- Used primarily in abdomen/thoracic cavity - Has outer sleeve with small holes to prevent tissue from becoming entrapped in the tip |
| Poole Suction Tip |
|
- Used most commonly in orthopedic and neurologic sx
|
| Frazier Suction Tip |
| - General purpose suction tip |
| Yankauer Suction Tip |
|
- Come in various sizes - Can be used to hold sterile saline for the surgeon's use during sx - can also be used to contain surgery samples so they don't get lost on the instrument tray |
| Stainless Steel Bowl |

|
| Poole Suction Tip |

|
| Frazier Suction Tip |

|
| Yankauer Suction Tip |
| Surgical Instruments for ID |



