|
Atom |
|
-Atom is the smallest unit of an element. -Mainly made of neutron, proton and electron.
Example:
|
|
Element |
|
-Element is a type of atom, a substance that cannot separated into simpler substance. Example: O, H, C, Cu, Fe, etc.
|
|
Molecule |
|
-A group of atoms combine together.
ex) H2O, CO2:
|
|
Compound |
|
-Compound is a pure substance bonded together by molecule.
ex) Ice____lots of water(H2O) molecule bonded together and frozen.
|
|
Subatomic particle |
|
-Smaller particle that formed nuclei and atoms.
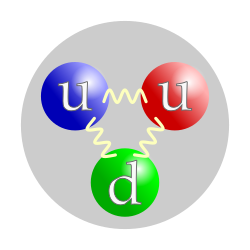
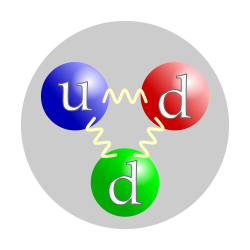
ex) Proton, neutron, electron. -Protons and neutrons formed nuclei. -Protons are made by 2 up quarks and a done quark. -Neutrons are made by 2 down quarks and a up quark. Proton(up) and Neutron(down)
|
|
Nucleus |
|
-A part of atom that is densely packed protons and neutrons.
ex)
|
|
Proton |
|
-Subatomic particle that have a positive charge.
ex.) Lithium(Li) atom has 3 protoms, therefore the charge of nucleus is +3 |
|
Neutron |
|
-Subatomic particle that have no charge.
ex.)Beryllium atom has 4 protons and 5 neutrons, but the charge of nucleus is only +4, therefore neutrons have no charge.
|
|
Electron |
|
-Subatomic particle that have a negative charge.
ex) see the diagram of "atom". -Nucleus is surrounded by electrons. An electron has a mass that's approximately 1/1836 that of the proton.
|
|
Atomic number |
|
-Organized the "thing" elements, same as the number of protons. -Found on the upper left corner of the periodic table.
ex) For hydrogen, the atomic number is 1 because it has one proton in each atom.
|
|
Ionic number |
|
-Combining capacity, metals: positive; non-metal: negative. -It's a positive or negative charge that an ion has.
ex) sodium ion has a charge of +1(metal); chlorine ion has a charge of -1(non-metal). |
|
Ion |
|
-The atom with charge(by lose or gain electrons), could be positive or negative.
ex) Sodium(see the diagram below), matal, easy to lose electrons.
When it lose the valent electron, it becomes ion.
|
|
Periodic table |
|
-A table to show chemical elements(well organized).
ex) |
|
Group/Family |
|
-Row of the periodic table. -They behave in similar ways, has the same nombers of electron on outer shell. -Difference: as going down, each element increases by 1 shell. -4 different families: Alkali metals, alkali earth metals, halogens, noble gases.(can be found on PR)
ex)H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr are in one group(group 1). |
|
Family |
|
|
|
Period |
|
-Across line of Periodic table.
ex)- elements increase by one proton -Same numbers of shell goint across. -see the diagram of "periodic table" |
|
Metal |
|
-Elements that found on left side of periodic table. -Given electrons and ion charge is positive.
ex) Cu, Fe, Hg........ |
|
Non-metal |
|
-Elements found on right side of PT. -gain electrons and the ioncharge is negative
ex) C, N, O, Ne, S etc. |
|
Atomic Mass |
|
-Velative mass mostly protons and neutrons. -Below of an element pic.
ex)Carbon
the # at the bottom is the atomic mass.
|
|
Valence shell &electrons |
|
-Valence Shell:The outer shell of an atom of bohr model. -Valence electron: the electrons on the valence shell.
ex) Sodium(Na)
The outer shell of this model is valence shell, and there're one valence electron on the outer shell. |
|
Stable |
|
-A chemical property to describe an element has a full electrons on the valent shell, don't react.
ex) Noble gases are stable. |
|
Bohr model |
|
-A model describes the element(atom). -Shows all the rings, electrons including valent electrons.
ex) Aluminium(Al) bohr model
|
|
Lewis model |
|
-A model describes the atoms. -Only shows valence electrons -Much easier than Bohr model.
ex)Carbon(C)
|
|
Ionic compound |
|
-Metal and non-metal connection, gain/lose electrons.
ex) The sodium(Na) ion and chlorine(Cl) ion:
(Sodium left and chlorine right.)
|
|
Covalent compound |
|
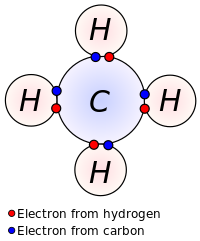
-Non-metal and non-metal connection. -Sharing electrons.
ex) CH4 (Carbon and hydrogen)
|
|
Naming |
|
-the name of element.
ex) AlCl3 naming: Aluminium chloride CO2 naming: Carbon dioxide
|
|
Formula |
|
-Shows how many elements does it make up, use symbol to describe.
ex) Sodium oxide: Na2O |
|
Unpaired electron |
|
-The electrons aren't paired yet(single, found in valent shell)during the covalent bonding. |
|
Long pair&Bond pair |
|
-Long pair: electrons in the valence shell of an atom during covalent bonding. -Bond pair: have electrons paired after compound.
ex)
|
|
Diatomic molecule |
|
-Diatomic molecules are molecules composed only of two atoms, of either same or different atoms.
ex) 8 common: F2, H2, O2, N2, Br2, At2, Cl2, I2 |
|
Cation/Anion |
|
-Cation: Ion with a positive charge. -Anion: Ion with a negative charge.
ex) Cation: Metals Anion: Non-metals. |
|
Equation |
|
- An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. -Chemical equation is a statement that describe how chemical reacts.
ex) 2H2+O2→2H2O
|
|
Physical & Chemical change |
|
-Physical change: a change with no new bonds -Chemical change: Make sth new.
ex) Physical change: Ice→water→steam -water frozen, ice melt...but still water. Chemical change: 2H2+O2→2H2O
|
|
Catalyst |
|
-Catalyst is a material that can speed up the chemical reaction/increase the rate of reaction.
ex) enzyme is a catalyst, when H2O2 reacts, MnO2 can be a catalyst. |
|
pH scale |
|
-A number scale from 1-14 -Tells if it's an acid or base -1=strong acid, 14=strong base, 7=neutral
ex)
|
|
Indicator |
|
-A chemical detector of protons in acid-base titration.
ex) Metyl Orange(red→yellow) Metyl red(red→yellow) Litmus(red→blue) Bromothymol blue(yellow→blue) |
|
Acid |
|
-Substance that have a pH that is less than 7. -All contain a hydrogen atom. ex) HCl, CH3COOH, H2SO4..... |
|
Base |
|
-Substance that have a pH that is greater than 7. -All base have hydroxide. -Some bases are much stronger than others. Those that are called caustic.
ex) NaOH, Mg(OH)2, NH4OH...... |
|
Naming Acid |
|
-if there's no oxygen, take beginning of both elements(usually hydro is the first element), add the ending "-ic" acid -If there is oxygen with an -ate ending, take second word and change ending to "-ic acid". -If there's oxygen with an -ite ending, take second word and change ending to "-ous acid"
ex) HCl: hydrogen chloride HClO4: Perchloric acid HClO2: Chlorous acid
|
|
Organic compound |
|
-An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecuel contain carbon.
ex) C2H5OH
|
|
Endothermic & Exothermic reaction |
|
-Endothermic reaction is a reaction that energy absorbed. -Exothermic reaction is a reaction that energy released.
ex) Iron reacts with oxygen is an exothermic reaction; Mixing ammonium thiocyanate and barium hydroxide___endothermic reaction. |
|
Law of conservation fo mass |
|
-After the precipitation reaction, the mass of the products still equals the mass of the reactants. This demonstrates the Law of Conservation of Mass.
ex) two reactants react in a inclosed container, the mass won't change after the reaction.
|
|
Radioactive Decay |
|
-Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles. -The rate(how fast or slow) of radioactive dacay can be compared using a measurement called half-life(see at next card). Example:
|
|
Half-Life |
|
-The amount of TIME it takes 1/2 of the "stuff"(of a radioactive sample) to disappear(=decay) -The shorter the half-life, the faster the decay.
Example: If there're 100 C-14 atoms, after 5730 yrs, there're about 50 of them.(approximate) Then 5730 yrs is the half-life of C-14 |
|
Parent isotope/ Daughter isotope |
|
-Parent isotope: the one that decays. -Daughter isotope: one of the decay products. Example: C-14 decayed and produced N-14, therefore C-14 is the parent isotope and N-14 is daughter isotope.
|
|
Decay curve |
|
-If we were to graph the number of percentage of remaining parent nuclei versus time, we sould always end up with a certain pattern. We call these graph DECAY CURVE. -A graph shows the relationship between the time and the radioactive nuclei remaining, usually a curve. Example:
|
|
Radioactivity |
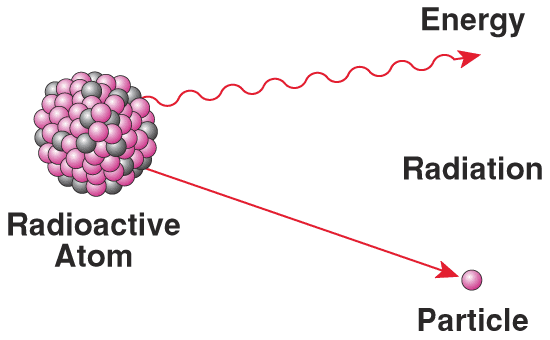
|
-Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of energy from unstable atoms.
-Radioactivity is the ejection of particles or radiation from the nuclear Example: -There're several type of radiation, the radiation from the sun for instance, have radioactivity.
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation |
|
-Electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation or EMR) is a form of energy emitted and absorbed by charged particles, which exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. -EMR has both electric and magnetic field components. Example: Light is a kind of EMR
|
|
Frequency/Wavelength |
|
-Frequency: the # of wavelength that pass a point in a sec. Measured in herz -Wavelength: The distance from a point on one wave to the same point on the next wave.
Example
|
|
Isotope |
|
-Atoms(individual) of the same element(type) that have different # of neutrons in the nuclei. -The weigh different amount.
Example Atomic mass=# of neutrons +Atomic number(# of protons) # of neutron=Atomic Mass-Atomic#
|
|
Graphing |
|
best-fit -Average line. -linear, curve(decay) Scale -use the entire sheet of paper -same amount of spaces -X and Y-axis can have different scales. ...Graph should have title , proper label and unit
|
|
Electrical repulsive force/Nuclear force |
|
-The nucleus is full of positive charge which repel each other(push each other away). This force is called electrical repulsive force.(ERF) -There 's also some force that holds it together called nuclear force(NR) -Stable: NR>ERF -Unstable: NR<ERF |
|
Alpha radiation/particles/ decay |
|
-Alpha radiation is a stream of alpha particles. -Alpha particles are positively charged atomic particles. -An alpha particle has the same combination of particles as a herlium nucleus. Example
|
|
Beta Radiation |
|
-Beta radiation is a radiation of beta particle during bet a decay. -Beta particle is an electron. We use the symbol ß or e in beta decay -Beta decay (ß):
|
|
Gamma Radiation |
|
-Gamma radiation consists of rays of high energy radiation. Has almost no mass and no charge. -The release of gamma radiation doesn't change the atomic number or the mass number of the nucleus. -The Gamma Ray is a high energy ray emitted from the nucleus. When a high-energy gamma ray is given off as the isotope falls from a high energy state to a low energy state.
Example:
|
|
Nuclear fission |
|
-a radioactive decay process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts (lighter nuclei), often producing free neutrons and photons (in the form of gamma rays), and releasing a very large amount of energy. Example:
-We can use the energy it released to generate electricity, also can be used for nuclear weapon.
|
|
Critical Mass |
|
-Smallest mass of radioactive substance possible to keep a chain reaction going.
|
| Nuclear Fusion |
|
-To fuse means to joining together. -Therefore the nuclear fusion is when small nuclei joined together to make a large nucleus. -Large amount of energy released.
Example: Hydrogen fusion: H-2+H-3→He-4+n(neutron)+Energy -The nuclei must collide at very high speed for the fusion to occur, or the repulsive forces will push them apart(100,000,000 degree is required) |