| Zygomatic process of frontal bone |
|
The structure indicated in red is the _____. |
| Parietal bone |
|
#9 is the _____. |
| Frontal bone |
|
#5 is the _____. |
| Occipital bone |
|
This entire bone is the ____. |
| External occipital protuberance |
|
This structure is the _____. |
| Superior nuchal line |
|
|
| Inferior nuchal line |
|
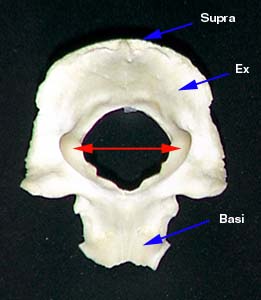
The structure inferior to the superior nuchal line is the _____. |
| Foramen magnum |
|
The structure #7 is the _____. |
| Occipital condyles |
|
The _____, located on either side of the foramen magnum, are the points at which the skull articulates with the atlas in the vertebral column. |
| Temporal bone |
|
The pink-colored bone is the _____. |
| Squamous portion of temporal bone |
|
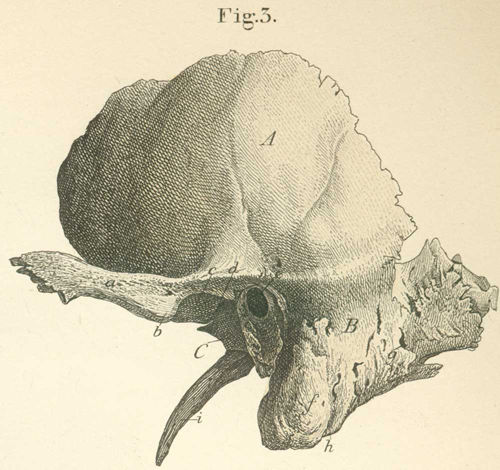
The structure labeled A, of the temporal bone, is the _____. |
| Petrous portion of temporal bone |
|
The ridge in the cranial floor that runs diagonally between the sphenoid and occipital bones; contains the middle and inner ear structure is the _____. |
| Mastoid portion of temporal bone |
|
The roughened, posterior portion of bone located behind the ear is the _____. |
| Zygomatic process of temporal bone |
|
The anterior extension from lower squamous portion indicated in Chinese is the _____. |
| Styloid process of temporal bone |
|
The narrow projection from the junction of the tempanic and petrous portions that is the attachment point for ligaments and muscles that control the hyoid bone, tongue, and parnx is the _____ (indicated as #6). |
| Mastoid process of temporal bone |
|
The large protrusion lateral to the styloid process and posterior to the external auditory meatus is known as the _____(indicated by #17). |
|
Mandibular fossa |
|
The depression in the the squamous portion below the zygomatic process; where the mandibular condyle articulates is the _____(indicated by #9). |
| Caratoid foramen/canal |
|
The hole on the anterior surface of the petrous portion anterior to the jugular foramen is the _____ (indicated by #23). |
| Jugular foramen/canal |
|
The opening along the junction between the petrous portion of the temporal bone and the occipital bone is the _____ (indicated by #22). |
|
Mastoid foramen
|
|
The hole posterior to the mastoid process that may not always be present or in the same location is the _____ (indicated by #13). |
| Stylomastoid foramen |
|
The small hole on the mastoid portion between the styloid and mastoid process is the _____ (indicated by #11). |
| External acoustic meatuses |
|
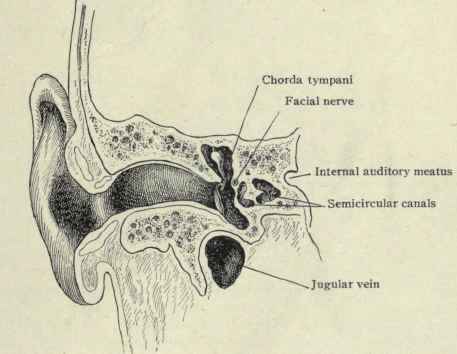
The opening along the external surface of the temporal portion is the _____. |
|
Internal acoustic meatus
|
|
The hole along the posteriormedial surface of the petrous portion is the _____ (indicated by #22). |
| Temporal fossa |
|
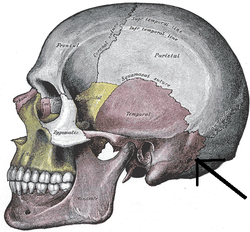
The large indentation on the side of the head is the _____ (indicated by the square). |
| Sphenoid bone |
|
The butterfly shaped cranial bone located in the middle of the skull between the frontal and temporal bones is the _____ (indicated in red). |
| Sella turcica |
|
The _____ is a saddle shaped housing for the pituitary gland. |
| Greater wings |
|
The prominent wing-like lateral extension from the body of sphenoid indicated in the image is the ______. |
| Lesser wings |
|
The small lateral extension from the sphenoid body, superior to the greater wing is the _____. |
| Chiasmatic groove |
|
The structure indicated by #7 is the _____. |
| Pterygoid processes |
|
The inferior extension from the junction of the sphenoid body and greater wing is _____ (indicated by #6). |
|
Pterygoid hamulus (s) Pterygoid hamuli (p)
|
|
The structure indicated by #19 is the _____. |
| Superior orbital fissure |
|
The elongated, narrow opening that runs diagonally along the back of the orbit between the lesser and greater wings is the _____ (indicated by #25 and #1).
|
| Foramen ovale |
|
The oval hole, superior to the foramen spinosum, in the greater wing, is the _____ (indicated by #25) |
| Forman spinosum |
|
The small opening posterior/inferior to the foramen ovale is the _____ (indicated by #24) |
|
Foramen rotundum
|
|
The round hole located anterior to the foramen ovale is the _____ (indicated by #12). |
| Optic foramen/canal |
|
The opening along the junctions of the lesser wing and body is the _____ (indicated by #10 above and #3 below).
|
| Ethmoid bone |
|
The _____ is a spongy, cuboid-shaped cranial bone located at the top of the nasal cavity and between the two orbits. |
|
Cribriform plate
|
|
The _____ (indicated by #4) is a horizontal plate in the cranial floor and roof of nasal cavity that articulates with the frontal bone.
|
| Olfactory foramina |
|
The tiny holes near the cribriform plate are called _____. |
| Perpendicular plate |
|
The thin vertical plate that extends down into the nasal cavity and articulates with the vomer bone to form the bony septum is the _____ (indicated by #4). |
| Crista galli |
|
The thin vertical plate that extends up from the cribriform plate and is the attachment point for the falx verebri is the _____ (indicated by #3). |
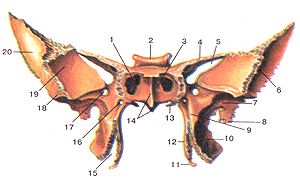
| Nasal bone(s) |
|
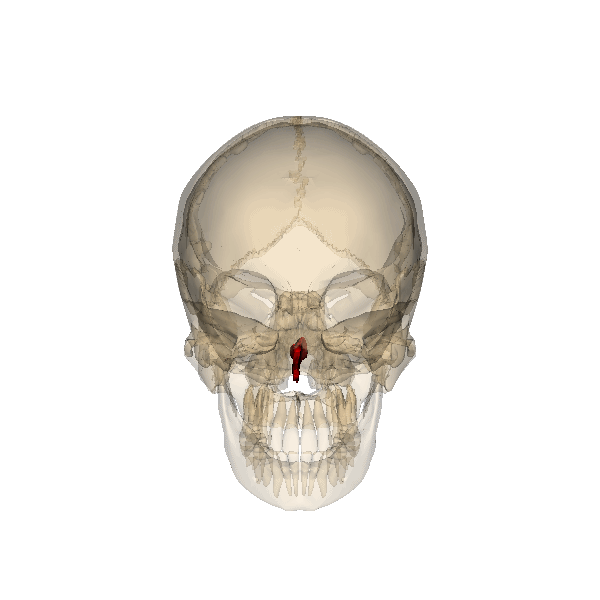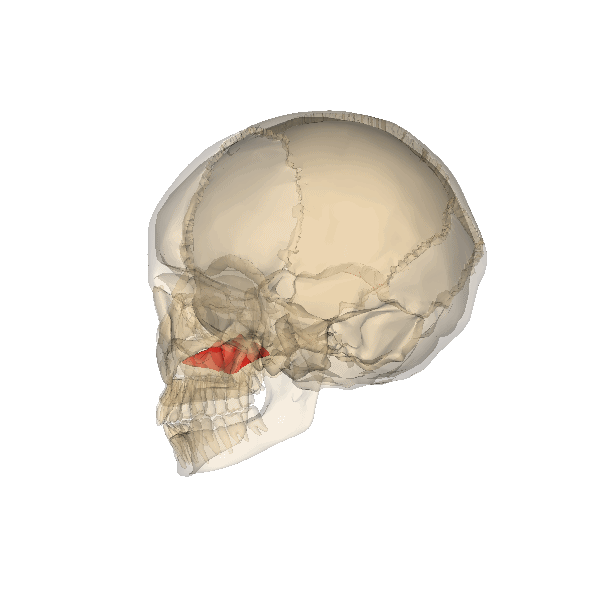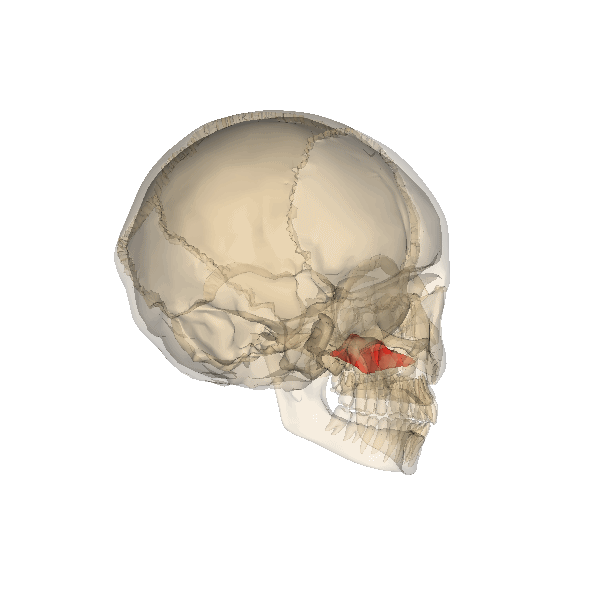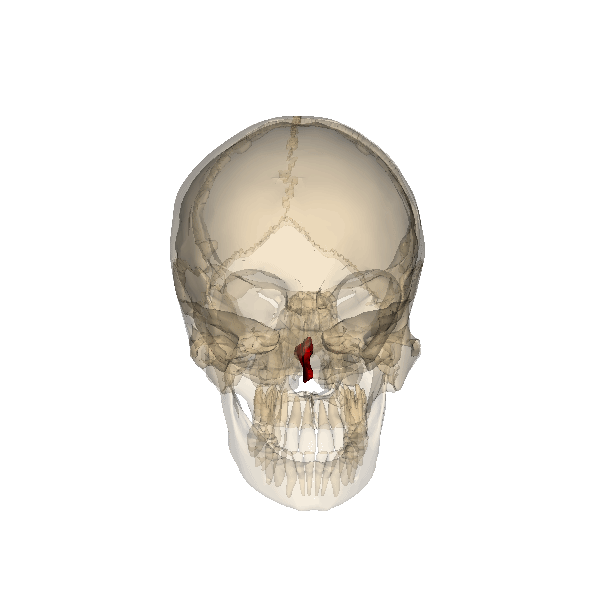
Two small bones that form the bridge of the nose are _____ (indicated in red). |
| Vomer bone |
|
The thin bone that runs vertically along the middle of the nasal cavity and articulates with the perpendicular plate is the _____ (indicated in red). |
| Lacrimal bone |
|
The _____ (indicated in red) is a small facial bone that forms a portion of the anterior medial wall of the orbit. |
| Maxilla (maxillary bones) |
|
The _____ (indicated in red) form the upper jaw. |
| Incisive foramen |
|
The _____ is a depression along the junction of the two maxillae bones, just posterior to the incisors. |
| Infraorbital foramen |
|
The _____ (indicated by #5) is a prominent hole located inferior to the orbit. |
| Zygomatic process of maxilla |
|
The lateral extension from the body of maxilla that projects toward the zygomatic bone is the _____. |
| Palatine bone(s) |
|
The _____ form portions of the hard palate, lateral walls of the nasal cavity, and floors of the orbits. These small L-shaped facial bones are located between the palatine processes of the maxilla bones and the pteryoid bones |
| Grater palatine foramen |
|
The largest opening along the posterior part of the horizontal plate is the _____ (indicated by #4). |
| Zygomatic bone(s) |
|
The two facial bones that form the cheeks and the lateral walls of the orbits are the _____. |
| Temporal process of zygomatic bone |
|
The projection that articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal bones to form the zygomatic arch is the _____. |
| Maxillary process of zygomatic bone |
|
The projection that articulates with the maxilla bone is the _____ (indicated in red). |
| Mandible |
|
The facial bone that forms the lower jaw and contains the lower teeth is the _____. |
| Ramus of mandible |
|
The posterior vertical portion of the mandible is the _____ (indicated by #11). |
| Angle of mandible |
|
The region of the mandible where the ramus and the body join is the _____ (indicated by #5). |
| Condyloid process (Mandibular condyle) |
|
The rounded head of the condylar process that articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone is the _____ (indicated by #1). |
| Coronoid process of mandible |
|
The sharply angled anterior extension from the mandibular ramus is the _____ (indicated by #3). |
| Body of mandible |
|
The _____ (indicated by #7) is the horseshoe shaped, anterior portion of the mandible. |
| Mandibular notch |
|
The prominent downward curvature between the condylar and coronoid processes is the _____ (indicated by #2). |
| Mandibular foramen |
|
The hole on the medial interior surface of the mandibular ramus is the _____ (indicated by #11). |
| Mental foramen |
|
The hole on the anterior aspect of the mandible below the second pre-molar is the _____ (indicated by #9). |
| Ear ossicles |
|
The bones of the inner ear are _____. |
| Malleus |
|
The bone of the inner ear shaped like a hammer that articulates with the incus is the _____ (indicated by #3). |
| Incus |
|
The bone of the inner ear that looks like an anvil and articulates with the malleus and stapes is the _____ (indicated by #2). |
| Stapes |
|
The inner ear bone that articulates with the incus and looks like a stirrup is the _____ (indicated by #1). |
| Hyoid bone |
|
The small U-shaped bone that is located between the mandible and larynx and is anterior to the third cervical vertebra is the _____. |
| Sutures |
|
Junctions between the adjacent bones of the skull are called _____. |
| Coronal suture |
|
The junction between the frontal and parietal bones is the _____ (indicated by #1). |
| Squamous suture |
|
The junction between the parietal and temporal bones is the _____ (indicated by #10). |
| Lambdoid suture |
|
The junction between the parietal and occipital bones is the _____ (indicated by #8). |
| Sagittal suture |
|
The junction between the two parietal bones is the _____ (indicated by #8). |
| Sinuses |
|
The cavities in the bones of the face and cranium are the _____. |
| Sphenoid sinus |
|
Two cavities in the center of the sphenoid bone are called the _____. |
| Ethmoid sinus |
|
A collection of small cavities located between the orbits in the lateral masses of the ethmoid bone are the _____. |
| Maxillary sinus |
|
Two large cavities located in the body of the maxillary bones, on either side of the nasal cavity are the _____. |
| Frontal sinus |
|
Two cavities located just above the orbits and behind the superciliary arches are the _____. |
| Nasal septum |
|
The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and vomer make up the _____. |
| Zygomatic arch |
|
The zygomatic process of the temporal bone + the temporal process of the zygomatic bone make up the _____. |
| Hard palate |
|
The structure formed by the maxillary and palatine bones is the _____. |
| Orbit |
|
The spherical structure formed by the frontal, maxillary, lacrimal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, palatine, and zygomatic bones is the _____. |
| Inferior orbital fissure |
|
The structure that lies mostly between the maxilla and the sphenoid is the _____. |
| Temporal fossa |



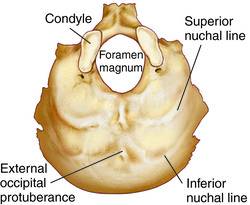

 The structure directly to the left/right of the external occipital process is the _____.
The structure directly to the left/right of the external occipital process is the _____.