|
Aegen art (kingdom order) |
| cycladic, minoan, and Mycenaen |

|
|
cycladic figure woman/male abstract found in graves marble 2500-2000 |

|
|
Kamares Ware Crete minoan
|

|
|
Palace at knossos Minoan Home of King minos and Theseus (greek hero that battled minotaur) In Crete Central court surrounded by fairly in fortified grouping of buildings/ system of terracotta pipes/ bulbous columns
filled with fresco's (arthor evens evacuated site)
|

|
|
Bull leaping from the palace at Knossos minoan true wet fresco
Man jumping boar
1400 BCE Bull leaping elongated figures with thin waist Shows both men in woman wet true fresco |
|
|
|
Snake goddesses Minoan from palace of Knossos Faience Hypnotic glaze Snake charmer cat on head |

|
|
Harvester Vase minoan Crete Steatite A libation vassal Overlapping figures muscular and skeletal structures Narrative |

|
|
Lion gate Mycenaean Used to scare off enemies corbelling
|

|
|
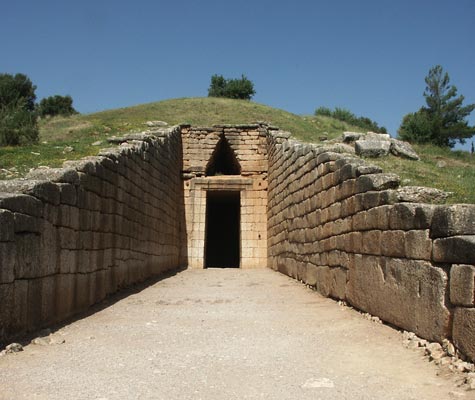
Treasury of Atreus Tholos beehive tomb men buried with weapons and cups Woman with jewelry Mycenaean |

|
|
Funerary Mark Mycenaean beaten gold
repousse death mask suggesting an attempt at capturing individualized features
repousse death mask suggesting an attempt at capturing individualized features |

|
|
dagger blade kept in the tombs Mycenaean
|
|
|
|
Warrior vase Mycenaean (krater- bowl for mixing wine with water) repetition without variety or excessive ornament |

|
|
Hermes and infant dionysos marble (bronze origional) from temple of Hera S-curve body soft playful Praxiteles |

|
|
Apoxyomenos Lysippos leaf cover up christianity s-curve
marble
|

|
|
Mosaics from Pella and were found mainly in two houses of the city, the "House of Dionysos" and the "House of the Abduction of Helen pebble moisics shows hunts
late classical |

|
|
battle of issus stone pebble mosiac depicting Greek defeat over Guals Hellenistic |

|
|
Corinthian order Hellenistic Most fancy
|

|
|
Agora Temple city planning Hellenistic
|

|
|
Alter of Zeus Hellenistic battle between gods and gaints alludes to the victory of king attalos 1 over the gauls
|

|
|
Dipylon Krator Geometric period (greek) Used as a grave marker overlapping figures
|

|
|
Mantiklos Apollo (very youthful) orientalizing absract no aurthor known bronze depicts apollo |

|
|
Lady of Auxerre daedalic style made up of many geometric shaes Orientalizing period note the hair greek marble still no Controposto |

|
|
Kouros/Kore archaic period begins to show naturalism archaic smile Chitin/peplos (kore garments)
|
|
|
|
temple of hera 1 made of heavy, closely spaced, cigar shaped columns. Doric order mostly distroyed, to honor hera archaic |

|
|
Siphnisn treasury and frieze sculpture lion attacking a person with a chariot and a person behind it colorful shows gigantomachy marble archaic |

|
|
francois vase archiac found in an etruscan tomb many mythological figures are shown krater shows both geometric and orientalizing features |
|
|
|
black figure/red figure pottery exekias archaic called a bilingual pot shows ajax and archilles playing cards |

|
|
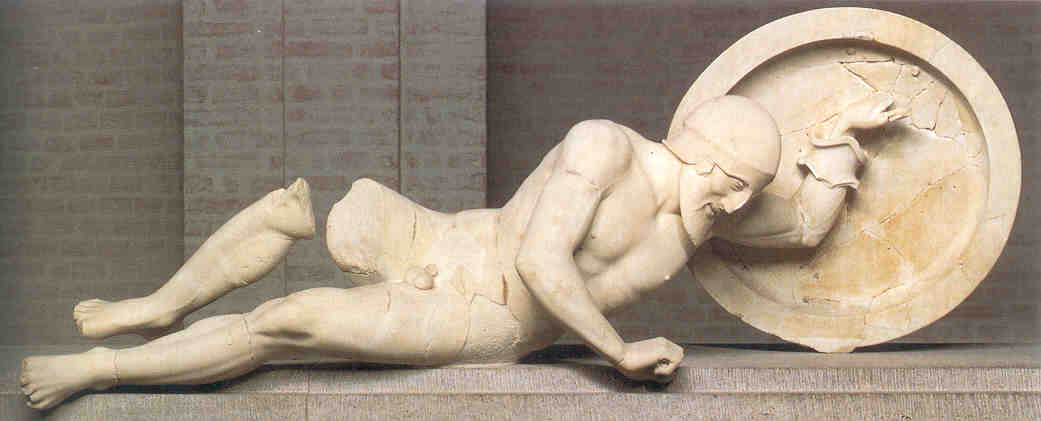
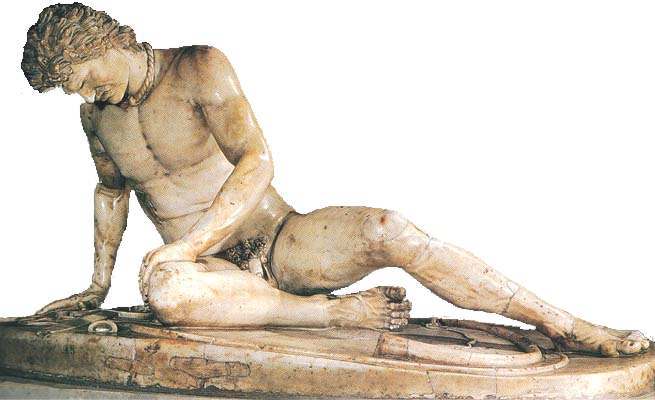
dying warrior - temple of Aphaia early classical body lying down more motion (natural posture) looking other way
|

|
|
Temple of hera 2 modeled afer zues's temple at Olympia doric early classical pediment part of a chariot race
|

|
|
sculpture, temple of Zeus, Olympia big / goldlike natural early classical
|
|
|
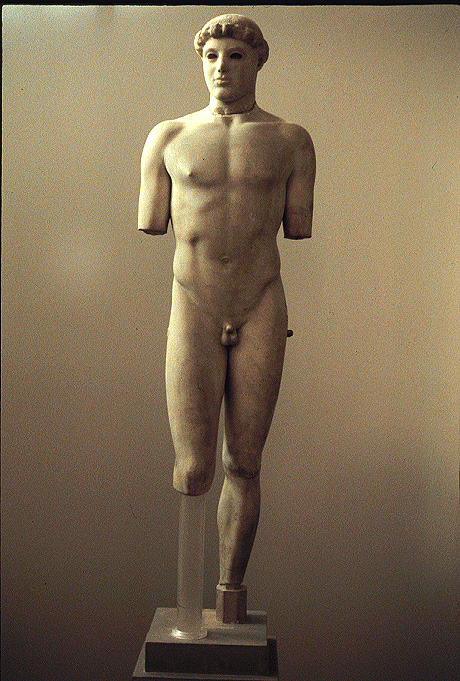
kritos boy no more archaic smile first sign of contraposto natural standing early classical
|

|
|
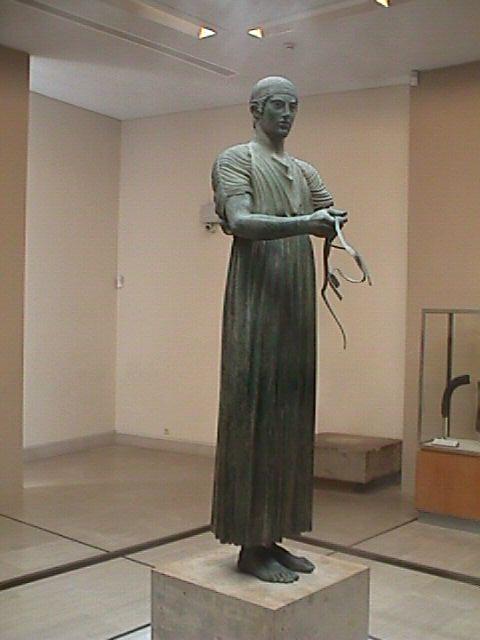
charioteer (delphi) circe perdue made like raice warriors bronze was a full chariot set no contraposto stiff, early classical |

|
|
discobolos myron shows motion lost origonal orig: bronze new: marble early classical |

|
|
Doryphoros Polykleitos Canon's proportion contraposto motion early classical bronze |

|
|
Acropolis (athens) on a hill made up of the parthenon, erechtion, and temple of athena nike after anthens burned down early classical |

|
|
parthenon created by mathmatical proportions iktinos and kallikrates doric classical ionic frieze
|

|
|
panthenaic procession (ionic frieze) East pediment depicting birth of Athena!! West depicting the contest of Poseidon and Athena reliefs
|

|
|
sculpture of Athena (by phidias) used to honor athena for the gift of the olive tree made of gold and ivory holding nike staff (victory) in her hand |

|
|
Erectheion / porch of maidens party of the acropolis early classical ionic caryatids (woman columns)
|

|
|
temple of athena nike used to honor athena 1 cella to honor the gods ionic
|

|
|
grave stele of hegeso shows commoner buying jewery a grave marker classical daily life shown |

|
|
aphrodite figures praxiteles first female nude goddess of live everyday life (realism) bathing late classical shy by covering herself |

|
|
theatre of epidauros place of gathering and entertainment on hillside late classical
|

|
|
tholos temple a shrine to the gods round doric outside/ corinthian inside late classical
|
|
|
dying Gual shows pain hellenistic portrayed by mustaches, neck bands, and bushy hair |

|
|
nike of Samothrace shows the goddess of victory realistic wind shown hellenistic
|

|
|
Aphrodite of Melos (venus de milo) teasing with lower portion covered eriotic marble hellenistic
|

|
|
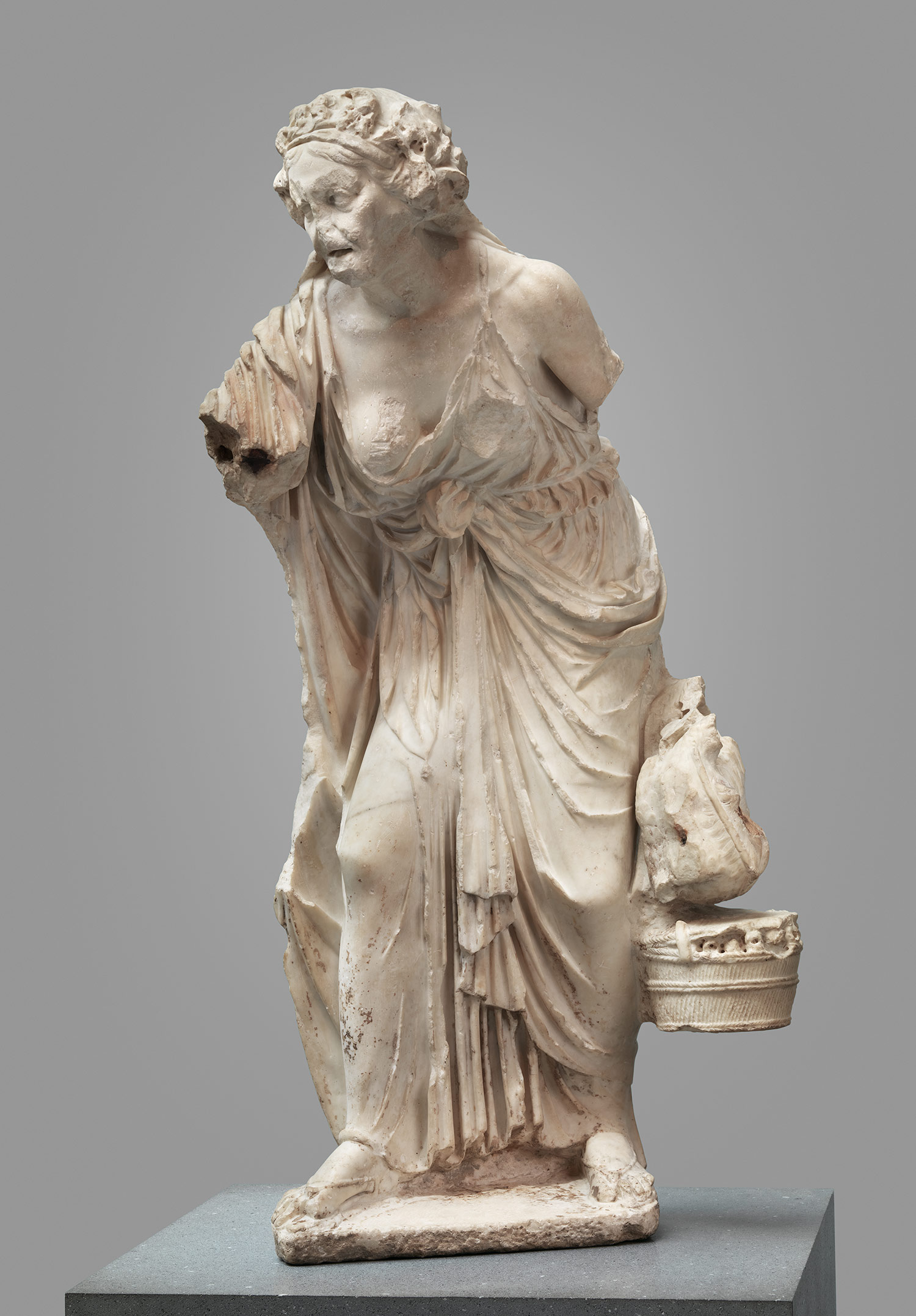
old market woman lower class old not normally shown detail in age hellenistic
|

|
|
laocoon shows lacoon fighting of serphant hellenistic motion /marble |

|
|
fibula with orientalizing lions etruscan shows orientalizing influene found in the tombs
|

|
|
temples/ model
|

|
|
apollo from veii more motion clothed detail in cloths controposto terra- cotta on temple roof |

|
|
necropolis : cerveteri tombs above ground tombs, made of natural materials you can actually walk into them, they have main doorways, everyday objects inside. ex bushes mirrors, fibula (fastening pin) (orientalizing period idea’s) idea of repousse and granulation etruscan
|

|
|
reclinging couple sarcophagus Etruscan terra- cotta, of man and woman together, woman had higher status , cremation, like sitting on a couch, reclining figures, man/wife liberal and free-spirited, woman had freedom (unlike greek) only civilization that value’s woman
|

|
|
capitloline wolf etruscan nursed by a she wolf- bronze, larger than life (realistic freestanding) linear lines. Context has watchful animal body, shows muscles, mistaken for Roman, the two kids are baby Remus and Romulus (founders of Rome) romulus king of rome. |
|
|
|
chimera of arezzo ( mythical monster - lion head and goat head) depiced as a composite animal, animated and ferocious etruscan
|

|
|
aule metele bronze Etruscan wears roman cloths orator
|

|
|
temples of fortuna, virilis republic era in Rome combined Greek and Etruscan ideas ionic staircase only in front |

|
|
sanctuary of fortuna roman republic concreate made up of barrel vaults, terraces, ramps, shops, and porticos. A tholos temple on top |

|
|
style 1 geometric shapes called the masonry style trys to imitate marble panels using stucco relief greek origion
|

|
|
2nd style depicts pictures/ mysteries wants a 3d world frieze |

|
|
style 3 has a small picture framish picture on the inside/ otherwise solid color |

|
|
style 4 a mix of the first styles background with the images of the 2nd style and then has the small pictures of the 3rd style |
v
|
|
fresco/mosaics of pompeii managed to preserve entire city due to volcanic explosion - mount Vesuvius- basilica adjacent to a forum/ decumanus and cardo - tells stories |

|
|
augustus of primaporta and livia Augustus- bronze - classical greek style , never ageing, armor, a general, son of a god livia- hairstyle changes, but never her face. no age. looks like a goddess early roman |

|
|
ara pacis augustae inspired by parthenon frieze, shows reconizable people like children propoganda to promote child bearing
early roman |

|
|
maison carree in france Greek corinthian capitals set on a high podium front entrance emphasized walls of cella pushed out to meet the engaged columns , interior expanded to the maximum size allowed beyond the porch used as a model for the jefferson state capital early roman |

|
|
pont du gard aquaducts ashlar masonry brings water/ proves Roman supremacy has keystone holding it up early roman heavy arches on bottom light on top |

|
|
colosseum actual name is flavian amphitheature room for 50000people concrete core, brick casing , travertine facing. 76 entrences and exits circle facade interplay of barrel vaults, groin vaults, and arches ment for entertainment early roman
|

|
|
portraits, vespasian, flavian woman marble idealized beuty long neck, tilted head cutting edge fashion hair shows light and shadow drill used to create hair early roman |

|
|
arch of titus early roman domitian erected this arch to honor titus victory spandrels around passageway trumpial arch victory over jewish wars |

|
|
imperial forum of trajan high roman built with spoils of dacien wars largest forum had equestrian statue of emperor, statues of dacian captives, two libraries, and a basilica
|

|
|
column and arch of trajan has reliefs on both facades advertising billbord showing emperors achievements
high empire |

|
|
pantheon dedicated to all gods corinthian capital porch in front two pediments drain water has huge oculus statues of the gods everywhere big gathering place high empire |

|
|
hadrian bust first guy to wear a beard- big thing lover of all greek bust - marble classical greek statues high empire |

|
|
petra a treasury high empire rock cut tomb used greek ideals |

|
|
marcus aurelius Antoninies high empire equestrian portriat shown as a conqorer bronze |

|
|
funerary art tons of layers a sarcophagus shows a story burial over cremation themes of greek mythology, fighting |

|
|
heroic portrait of trebonianus gallus Severian bronze over- life - size nude brute force powerful old man |

|
|
ludovisi battle sarcophagus Chaos battle between roman and barbarians. rejection of classical perspective. extremely overcrowded with figures overlapping figures lack individuality confusion of battle is echoes by congested composition bearded roman army trounces and defeates barbarians marble |

|
|
four tetrarchs, porphyry shows the 4 kings that rome got broken into porphyry - purple faces and everything looks simular shapeless bodies beneath cloaking drapery late empire |

|
|
arch of constantine late empire showed great old empires and his achievements 3 arches |