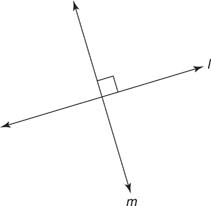
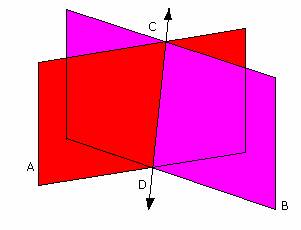
| The intersection of to lines is a ... |
|
point
|
| angle |
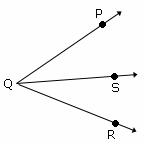
A figure formed by two rays with a common endpoint.
|
| collinear |
Points lying on the same line.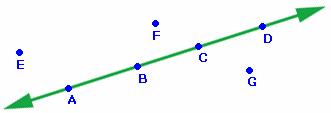
|
| coplanar |
Points lying on the same plane.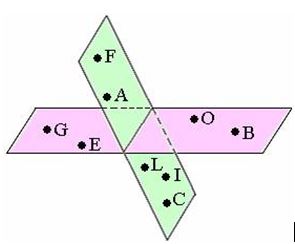
|
| intersect |
Two or more points in common.
|
| line |
An undefined term in geometry, understood to be perfectly straight, has no thickness, contain and infinite amount of points, and extend infinitely in both directions.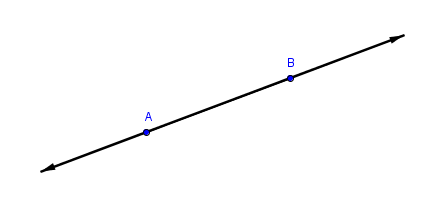 s. s.
|
| plane |
|
An undefined term in geometry, which is understood to be a flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions.
|
| point |
An undefined term in geometry, that can be thought of as a dot that represents a location in space that has no size.
|
| postulate |
| A statement that is accepted as true without proof. |
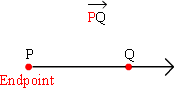
| ray |
|
A part of a line that starts at a point and extends infinitely in one direction.
|
| segment |
A part of a line that begins at one point and ends that another.
|
| vertex of an angle |
The point in common of the two rays that form an angle.
|
| The intersection of two planes is a ... |
|
line.
|
| Through any two points there is one and only ... |
|
line . |
| Through any three noncollinear points there is one and only one... |
|
plane.
|
| If there are two points in a plane, then the line containing them is in the ... |
|
plane.
|
| congruent |
|
The relationship between figures having the same size and shape.
|
| length |
|
The distance from one endpoint to another. abs val ( a - b ) or abs val ( b - a ) |
| Segment Congruence Postulate |
|
If two segments have the same length as measured by a fair ruler, then the segments are congruent. Also, if two segments are congruent, then they have the same length as measured by a fair ruler. |
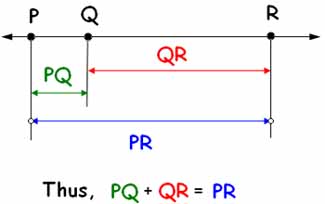
| Segment Addition Postulate (line including points PQR) |
|
If point Q is between points P and R on a line, then PQ + QR = PR
|
| acute angle |
|
An angle whose measure is less than 90 degrees.
|
| complementary angles |
|
Two angles whose measure has a sum of 90 degrees.
|
| linear pair of angles |
|
These angles are created when two lines intersect. The measure of the line is 180 degrees, so the angles must also sum 180 degrees.
|
| obtuse angle |
|
An angle whose measure is greater than 90 degrees.
|
| right angle |
|
An angle whose measure is 90 degrees.
|
| supplementary angles |
|
Two angles whose sum has a measure of 180 degrees.
|
| Angle Addition Postulate |
|
Angle Addition Postulate states that if a point S lies in the interior of ∠PQR, then ∠PQS + ∠SQR = ∠PQR.
|
| Angle Congruence Postulate |
|
If angles have the same measure, then they are congruent. If two angles are congruent, then they have the same measure.
|
| Linear Pair Property |
|
If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary.
|
| angle bisector |
|
A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles.
|
| center of rotation |
|
The point at which an image rotates around.
|
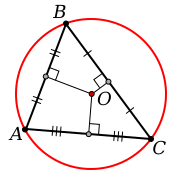
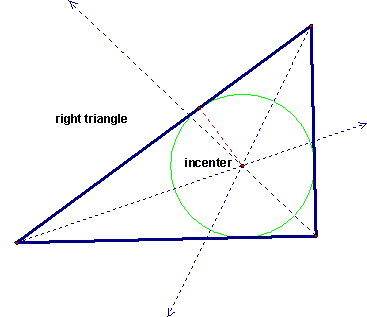
| circumcenter |
|
The center of a circumscribed circle; the point which the three perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle intersect.
|
| circumscribed circle |
|
A circule that is drawn around the outside a triagle and contains all three vertices.
|
| concurrent |
|
Literally, "running together"; of three or more lines, intersecting at a single point.
|
| conjecture |
| A statement that is believed to be true. |
| endpoint |
|
A point at an end of a segment or the starting point of a ray.
|
| incenter |
|
The center of an inscribed circle; the point where the three angle bisectors of a triangle intersect.
|
| inscribed circle |
|
Is a circle inside a triangle that touches each side of the triangle at one point.
|
| midpoint of a segment |
|
The point that divides a segment into two congruent segments.
|
| parallel lines |
|
Coplanar lines that never intersect.
|
| perpendicular bisector |
|
A line that is perpendicular to a segment at its midpoint.
|
| perpendicular lines |
|
Lines that intersect to form right angles.
|
| preimage |
| A shape that undergoes a motion or a transformation. |
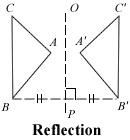
| reflection |
|
A transformation that creates a mirror image.
|
| rotation |
|
A transformation where the image is rotated around a single point.
|
| translation |
|
A transformation in which every point on the image moves/slides the same direction.
|
| rigid transformation |
| A transformation that does not change the shape or size of a figure. |




 .
.