|
Life in early hunter-gatherer societies
|
|
Homo sapiens emerged in east Africa between 100,000 and 400,000 years ago. Homo sapiens migrated from Africa to
|
|
Early human societies, through the development of culture, began the process of overcoming the limits set by the physical environment. What were the characteristics of huntergatherer societies?
|
|
Hunter-gatherer societies during the Paleolithic Era (Old Stone Age) • were nomadic, migrating in search of food, water, shelter • invented the first tools, including simple weapons • learned how to make and use fire • lived in clans • developed oral language • created “cave art.”
|
|
The beginning of agriculture, including permanent settlements, was a major step in the advance of civilization. How did the beginning of agriculture and the domestication of animals promote the rise of settled communities?
|
|
Societies during the Neolithic Era (New Stone Age) • developed agriculture (domesticated plants) • domesticated animals • used advanced tools • made pottery
• developed weaving skills.
|
|
How does archaeology provide knowledge of early human life and its changes?
|
|
Archaeologists study past cultures by locating and analyzing human remains, settlements, fossils, and artifacts. Archaeologists apply scientific tests, such as carbon dating, to analyze fossils and artifacts
|
|
What is Stonehenge?
|
|
Stonehenge is an example of an archaeological site in England that was begun during the Neolithic Age and completed during the Bronze Age.
|
|
What are Aleppo and Jericho?
|
|
Aleppo and Jericho are examples of early cities in the Fertile Crescent studied by archaeologists.
|
|
What is Çatalhöyük?
|
|
Çatalhöyük is an example of a Neolithic settlement currently under excavation in Anatolia.
|
|
Why did ancient civilizations develop in river valleys?
|
|
These river valleys offered rich soil and irrigation water for agriculture, and they tended to be in locations easily protected from invasion by nomadic peoples.
|
|
River valley civilizations (about 3500 to 500 B.C. [B.C.E.]) Where was the Mesopotamian civilization?
|
|
Tigris and Euphrates River Valleys (Southwest Asia)
|
|
Where was Egyptian Civilization located?
|
|
Egyptian civilization: Nile River Valley and Nile Delta (Africa)
|
| Where was the first Indian civilization located? |
|
Indian civilization: Indus River Valley (South Asia)
|
| Where was the first Chinese civilization located? |
|
• Chinese civilization: Huang He Valley (East Asia)
|
|
Why did ancient civilizations develop in river valleys?
|
|
| When did the earliest river valley civilizations emerge? |
| Between 3500 and 500 BCE (BC) |
| What area was settled by the Hebrews/Jews? |
|
Hebrews settled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River Valley (part of Fertile Crescent in Southwest Asia).
|
| Where did the Phoenicians settle? |
|
Phoenicians settled along the Mediterranean coast (part of Fertile Crescent in Southwest Asia).
|
| Where was Nubia located? |
|
Nubia was located on the upper (southern) Nile River (Africa).
|
|
What were the social characteristics of early civilizations?
|
|
Development of social patterns • Hereditary rulers: Dynasties of kings, pharaohs • Rigid class system where slavery was accepted
|
|
What were the politicalcharacteristics of early civilizations?
|
|
Development of political patterns • World’s first states (i.e., city-states, kingdoms, empires) • Centralized government, often based on religious authority • Written law codes (e.g., Ten Commandments, Code of Hammurabi)
|
|
What were the economic characteristics of early civilizations?
|
|
Development of economic patterns • Use of metal (e.g., bronze, iron) tools and weapons • Increasing agricultural surplus: Better tools, plows, irrigation • Increasing trade along rivers and by sea (Phoenicians) • Development of the world’s first cities • Development of the practice of slavery within most cultures in the ancient world, taking various forms
|
|
What religious traditions developed in ancient civilizations?
|
|
Development of religious traditions • Polytheism was practiced by most early civilizations. • Monotheism was practiced by the Hebrews.
|
| What is Monotheism |
| Worshipping only one God |
| What is Polytheism |
| Worshipping many different gods. |
| What man was the founder of Judiasm? |
| Abraham |
| This man led the Jews from their enslavement in Egypt during the Exodus. |
|
Moses
|
| This city was home to the temple of Solomon. |
Jerusalem
|
|
What were the essential beliefs of Judaism?
|
|
Beliefs, traditions, and customs of Judaism • Belief in one God (monotheism) • Torah, which contains the written records and beliefs of the Jews • Ten Commandments, which state moral and religious conduct
|
| How did Judaism spread? |
| Through exile and the Diaspora. |
| What are pictograms? |
| The earliest written symbols. |
|
What is this language?
|
| Cuneiform, it was the first written language and was developed in Sumer. |
|
What is this language which developed in Ancient Egypt? |
| Hieroglyphics |
| Which group created the first phoenitic alphabet, or alphabet based on sound. |
| The Phoenicians. |
| How did the Persian Empire treat its conquered peoples? |
|
Fairly. People were able to keep their own customs and religion. |
| Why did the Persian Empire develop and imperial bureaucracy? |
| To help govern the empire and make it more manageable. It was divided into Satrapies ruled by Satraps. |
|
Who was Zoroaster?
|
|
He was the founder of the Persian religion of Zoroastrianism.
Practice of Zoroastrianism – Religion of Persia – Belief in two opposing forces in the universe
|
| How did the Persians unite their vast empire. |
They build a road system called the Royal Road.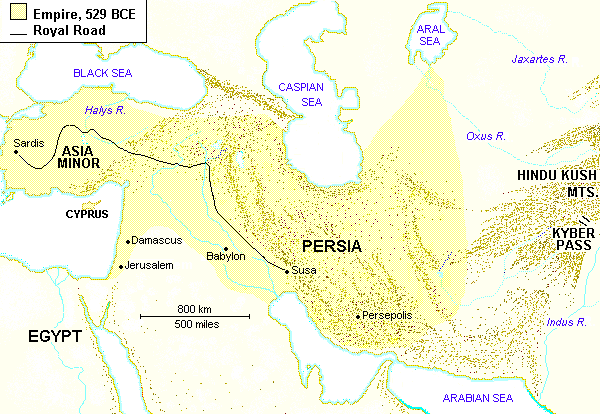
|
|
Why were physical geography and location important to the development of Indian civilization?
|
|
| What two cities made up the Indus Valley Civilization? |
Harappa and Mohenjo Daro
|
|
What impact did the Aryans have on India?
|
|
Aryans (Indo-Aryans) • Migration, assertion of dominance • Caste system, which influenced all social interactions and choices of occupations
|
|
Why was the caste system central to Indian culture?
|
|
Caste system, which influenced all social interactions and choices of occupations
|
|
What were the accomplishments of the Mauryan Empire?
|
|
Mauryan Empire - Asoka • Continued political unification of much of India • Contributions: Spread of Buddhism, free hospitals, veterinary clinics, good roads
|
|
What were the accomplishments of the Gupta empire?
|
|
Gupta Empire • Golden Age of classical Indian culture • Contributions: Mathematics (concept of zero), medical advances (setting bones), astronomy (concept of a round earth), new textiles, literature
|
|
What are the beliefs of the Hindu religion?
|
|
Hinduism • Belief in many forms of one God • Reincarnation: Rebirth based upon karma • Karma: Knowledge that all thoughts and actions result in future consequences • Vedas and Upanishads: Sacred writings • Spread along major trade routes
|
What are the beliefs of Buddhism?
|
|
Buddhism • Founder: Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) • Four Noble Truths • Eightfold Path to Enlightenment
|
| How did Buddhism spread? |
|
Asoka’s missionaries and their writings spread Buddhism from India to China and other parts of Asia.
|
|
Why was the Great Wall of China built?
|
|
Migratory invaders raided Chinese settlements from the north. Qin Shi Huangdi built the Great Wall as a line of defense against invasions.
|
| Why did Chinese rulers believe they had the power to rule? |
|
China was governed by a succession of ruling families called dynasties. Chinese rulers were considered divine, but they served under a Mandate of Heaven only as long as their rule was just.
|
| Why was the silk road important? |
|
The Silk Road facilitated trade and contact between China and other cultures as far away as Rome.
|
|
What were contributions of classical China to world civilization?
|
|
Contributions of classical China • Civil service system • Paper • Porcelain • Silk
|
|
Why were Confucianism, important in the formation of Chinese culture?
|
|
Impact of Confucianism in forming the social order in China • Belief that humans are good, not bad • Respect for elders • Code of politeness (still used in Chinese society today) • Emphasis on education • Ancestor worship
|
|
Why were Taoism important in the formation of Chinese culture?
|
|
Impact of Taoism in forming Chinese culture and values • Humility • Simple life and inner peace • Harmony with nature
|
|
What is this symbol? Why was it important? |
|
Yin and yang represented opposites for Confucianism and Taoism.
|
|
Why was Buddhism important in the formation of Chinese culture?
|
| Chinese forms of Buddhism spread throughout Asia. |
|
How did the mountains, seas, islands, harbors, peninsulas, and straits of the Aegean Basin shape Greek economic, social, and political development and patterns of trade and colonization?
|
|
Economic and social development • Agriculture (limited arable land) • Commerce and the spread of Hellenic culture • Shift from barter to money economy (coins) Political development • Mountainous terrain both helped and hindered the development of citystates. • Greek cities were designed to promote civic and commercial life. • Colonization was prompted by overpopulation and the search for arable land.
|
|
What body of water is represented by the letter E? |
| Aegean Sea |
|
What peninsula is Greece a part of?
|
| Balkan Peninsula |
|
The city state of Sparta was located on the ______________ peninsula. |
| Peloponnesus. |
|
Letter D is the city-state of: |
| Athens |
|
Letter J is the city of: |
| Troy |
|
Letter C is the ____________ Sea. |
| Mediterranean. |
|
Number 1 is the __________ Strait. |
| Dardanelles (Hellespont) |
|
Number 3 is the Peninsula: |
| Asia Minor |
|
How did mythology help the early Greek civilization explain the natural world and the human condition?
|
|
Greek mythology • Based on polytheistic religion • Offered explanations of natural phenomena, human qualities, and life events
|
|
Greek King of the gods and the god of Thunder.
|
| Zeus |
|
|
| Hera |
|
Greek god of the Sun. He was also the god of the arts. |
| Apollo |
|
Greek goddess of the Hunt, she is the twin sister of Apollo.
|
| Artemis |
|
Greek goddess of wisdom and the patron goddess of the city-state of Athens. |
| Athena |
|
Greek goddess of love and beauty
|
| Aphrodite |
|
What impact did Greek mythology have on later civilizations and the contemporary world?
|
|
Symbols and images in Western literature, art, and architecture
|
| What groups made up the membership of the Greek Polis? |
|
• Citizens (free adult males) had political rights and the responsibility of civic participation in government. • Women and foreigners had no political rights. • Slaves had no political rights.
|
| How did democracy develop in Athens? |
|
• Stages in the evolution of Athenian government: Monarchy, aristocracy, tyranny, democracy • Tyrants who worked for reform: Draco, Solon • Origin of democratic principles: Direct democracy, public debate, duties of the citizen
|
| How did Sparta differ from Athens? |
|
Sparta • Oligarchy (rule by a small group) 2 Kings, Ephors, Gerousia, and Assembly • Rigid social structure • Militaristic and aggressive society
|
|
Why were wars with Persia important to the development of Greek culture?
|
|
Importance of Persian Wars (499–449 B.C. [B.C.E.]) • Persian wars united Athens and Sparta against the Persian Empire. • Athenian victories over the Persians at Marathon and Salamis left Greeks in control of the Aegean Sea. • Athens preserved its independence and continued innovations in government and culture.
|
|
Why was the Peloponnesian War important to the spread of Greek culture?
|
|
Importance of Peloponnesian War (431–404 B.C. [B.C.E.]) • Caused in part by competition for control of the Greek world: Athens and the Delian League versus Sparta and the Peloponnesian League • Resulted in slowing of cultural advance and the weakening of political power
|
|
Why was the leadership of Pericles important to the development of Athenian life and Greek culture?
|
|
Golden Age of Pericles (mostly occurring between the Persian and the Peloponnesian Wars) • Pericles extended democracy; most adult males had an equal voice. • Pericles had Athens rebuilt after destruction in the Persian Wars; the Parthenon is an example of this reconstruction.
|
| What two playwrights contributed to Greek culture and Western Civilization? |
| Drama: Aeschylus, Sophocles |
| This man wrote the Iliad and Odyssey. |
| Homer |
| This man is considered the father of history. He wrote about the Persian Wars. |
| Herodotus |
| This man wrote the first objective history on the Peloponnesian War. |
| Thucydides. |
|
This man was the Greek sculptor who desiged the great statue of Athena inside
|
| Phidias |
| What are the three types of Greek columns. |
|
Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian
|
|
Greek temple to Athena which includes Doric Columns.
|
| The Parthenon |
| Greek father of medicine. |
| Hippocrates. |
| Greek scientist who worked with the lever and pulley . . . Eureka! |
| Archimedes. |
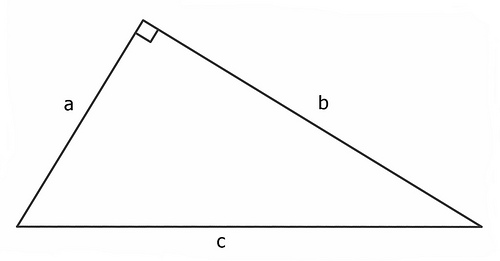
| This man wrote "The Elements" and is considered to be the father of Geometry. |
| Euclid. |
|
Greek mathematician who came up with this idea.
|
| Pythagoras. |
| Greek philosopher who said that people should "Know Themselves" and was put to death for corrupting the youth of Athens. |
|
Socrates
|
| Greek philosopher who was the student of Socrates. He wrote "The Republic" and believed in the world of forms. |
| Plato |
| Greek philosopher who was the student of Plato. He believed that knowledge was gained by observing the world around us and was the tutor of Alexander the Great. |
|
Aristotle. |
| This Macedonian conquered much of Greece prior to his assassination. |
| Philip II |
|
How did the empire of Alexander the Great establish a basis for the spread of Hellenistic culture?
|
|
Alexander the Great • Established an empire from Greece to Egypt and the margins of India • Extended Greek cultural influences
|
| What was Hellenistic Culture? |
|
Hellenistic Age • Blend of Greek and oriental elements • Spread of Hellenistic culture through trade
|
|
Rome was centrally located in this body of water. |
| The Mediterranean. |
| These mountains to the north of Italy helped protect the Italian Peninsula. |
| The Alps. |
| Rome was located on this peninsula. |
| The Italian Peninsula. |
| What did the Mediterranean Sea provide for the Roman civilization. |
|
Protection and sea borne commerce.
|
| What was the source for Roman Mythology? |
|
The Greeks and their mythology influenced the development of Roman Mythology. Roman mythology • Based on the Greek polytheistic religion • Explanations of natural phenomena, human qualities, and life events
|
Who was the king of the Roman gods? gods?
|
| Jupiter |
Who was the queen of the Roman gods and the Roman goddess of marriage? gods and the Roman goddess of marriage?
|
| Juno |
| Who was the Greek and Roman god of the Sun? |
|
Apollo
|
| Who was the Roman goddess of the hunt? |
| Diana |
| Who was the Roman goddess of love and beauty? |
| Venus |
| How does Roman mythology still influence us today? |
|
Symbols and images in literature, art, and architecture
|
| Who were the Patricians? |
| The upper-class of the Roman Republic. |
| Who were the Plebeians? |
| The Lower-Class of the Roman Republic. |
| Slavery in ancient Rome was not based on ____. |
| Race |
| What groups qualified for citizenship in the Roman Republic? |
|
Citizenship • Patrician and plebeian men • Selected foreigners • Rights and responsibilities of citizenship (e.g., taxes, military service)
|
| The Roman Republic was a __________ Democracy. |
| Representative. |
| This was the main assembly of the Roman Republic. |
| The Senate |
| The assemblies of the Roman Republic included: |
|
The Senate The Centuriate Assembly The Council of the Plebs. |
In the Roman Republic these men served together for one, one-year term.
|
| Consuls. |
| This was the first codification of Roman law. |
| The Twelve Tables. |
| Rome fought a series of three wars with Carthage known as the ______ Wars. |
| Punic |
| This general from Carthage invaded Rome in the Second Punic War. |
Hannibal
|
| What were the results of the Punic Wars? |
|
Three wars resulted in Roman victory, the destruction of Carthage, and expanded trade and wealth for Rome.
|
|
What was the evolution of the Roman Empire and spread of Roman culture
|
|
• Mediterranean basin (Africa, Asia, Europe, including the Hellenistic world of the Eastern Mediterranean) • Western Europe (Gaul, British Isles)
|
| What were some of the causes for the decline of the Roman Republic? |
|
• Spread of slavery in the agricultural system • Migration of small farmers into cities and unemployment • Civil war over the power of Julius Caesar • Devaluation of Roman currency; inflation
|
| After Marius made military reforms that allowed generals to rise to power what three generals made up the first Triumvirate? |
|
Crassus Pompey Julius Caesar |
Before Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BCE the Senate had appointed him _____ ____ ____. assassinated in 44 BCE the Senate had appointed him _____ ____ ____.
|
|
Dictator for Life
|
These events describe the life of what man?

|
| Augustus Caesar (Octavian) |
|
How was the Roman Empire unified and enlarged? |
|
Imperial Authority (Authority of the Emperor) and Military conquest.
|
| One of the reason for the failure of the Roman Empire is that they failed to provide for the peace succession of ______. |
| Emperors. |
| What was the Pax Romana? |
|
The Pax Romana • Two centuries of peace and prosperity under imperial rule • Expansion and solidification of the Roman Empire, particularly in the Near East
|
| What was the economic impact of the Pax Romana? |
|
• Established uniform system of money, which helped to expand trade • Guaranteed safe travel and trade on Roman roads • Promoted prosperity and stability
|
| What was the social impact of the Pax Romana? |
|
Social impact of the Pax Romana • Returned stability to social classes • Increased emphasis on the family
|
| What was the political impact of the Pax Romana? |
|
Political impact of the Pax Romana • Created a civil service • Developed a uniform rule of law
|
| What were the origins of Christianity within the Roman Empire? |
|
Origins of Christianity • Had its roots in Judaism • Was led by Jesus of Nazareth, who was proclaimed the Messiah • Conflicted with polytheistic beliefs of Roman Empire
|
|
What were the essential beliefs of the early Christian faith?
|
|
• Monotheism •Jesus as both Son and incarnation of God
|
| How and why did Christianity spread? |
|
|
|
What was the impact of the early Church in the late Roman Empire?
|
|
Impact of the Church of Rome in the late Roman Empire • The Emperor Constantine converted to Christianity and made it legal. • Christianity later became the official state religion. • The Church became a source of moral authority. • Loyalty to the Church became more important than loyalty to the Emperor. • The Church became the main unifying force of Western Europe.
|
|
What is this Roman Structure, it was the center of the Roman city?
|
| The Forum |
|
This Roman building was a temple built by the Emperor Hadrian to honor all of the Roman gods.
|
| Pantheon |
|
This Roman structure was the site of great spectacles for public entertainment.
|
| The Colosseum |
The Romans built thousands of miles of these to connect their empire, some are still in use today.
|
|
Roads
|
|
These structures brought water into Roman cities.
|
| Aqueducts |
|
This Roman architectural innovation allowed them to span large areas using less building material. |
| Roman Arch |
| This Roman scientist stated that the Earth was the center of the Universe, a view we call Geocentric. |
|
Ptolemy
|
| What were some of the Roman medical innovations? |
|
Emphasis on public health (public baths, public water systems, medical schools)
|
| The Roman empire used Latin as its primary language. What are the languages based on Latin called? |
|
Romance languages.
French, Spanish, and Italian are examples.
|
| Roman epic written by Virgil. |
|
The Aeneid
|
| Rome originally used mythology as its religion. What religion did Rome adopt in the third century CE? |
|
Christianity.
|
| What legal principle do we get from the Romans. |
| The concept that you are innocent until proven guilty, from the Twelve Tables. |
| What were some of the causes for the fall of the Roman Empire? |
|
Causes for the decline of the Western Roman Empire • Geographic size: Difficulty of defense and administration • Economy: The cost of defense, and devaluation of Roman currency • Military: Army membership started to include non-Romans, resulting in decline of discipline • Moral decay: People’s loss of faith in Rome and the family • Political problems: Civil conflict and weak administration • Invasion: Attacks on borders
|
| Where did the Roman Emperor Constantine move the capital of the Roman Empire? |
| To Byzantium, which was renamed Constantinople. |
| When did the Western Roman Empire fall? |
| 476 CE |
| After the Western Empire fell the Eastern Empire continued as the ___________ Empire. |
| Byzantine. |
|
Why was Constantinople established as the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire?
|
|
Location of Constantinople • Protection of the eastern frontier • Distance from Germanic invasions in the western empire • Crossroads of trade • Easily fortified site on a peninsula bordered by natural harbors
|
| What was the new role of Constantinople? |
|
Role of Constantinople • Seat of the Byzantine Empire until Ottoman conquest • Preserved classical Greco-Roman culture • Center of trade
|
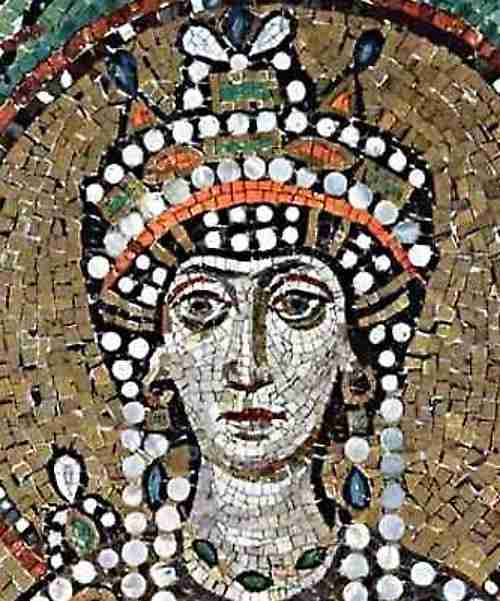
What were the major accomplishments of the Byzantine Emperor Justinian? Justinian?
|
|
Byzantine Emperor Justinian • Codification of Roman law (impact on European legal codes) • Reconquest of former Roman territories • Expansion of trade
|
| What factors inspired Byzantine Art and Architecture? |
| Christianity and Imperial Power. There were many images of religious figures and kings. |
What were icons?
|
| Religious images, prominent in Byzantine (Eastern) Churches. |
|
The Byzantines frequently used this art form to decorate their Churches and buildings. It is made from small pieces of glass or tile.
|
| Mosaic |
|
This great domed church was built by the Emperor Justinian?
|
| Hagia Sophia |
|
How did Greek and Roman culture survive within the Byzantine Empire?
|
|
Byzantine culture • Continued flourishing of Greco- Roman traditions • Greek language (as contrasted with Latin in the West) • Greek Orthodox Christianity • Greek and Roman knowledge preserved in Byzantine libraries
|
| What were the characteristics of the Eastern/Orthodox Church? |
|
Eastern Church • Centered in Constantinople • Close to seat of power after Constantinople became capital • Use of Greek language in the liturgy
|
| What were the characteristics of the Western Church? |
|
|
|
What factors produced the division (The Great Schism) within the Christian Church?
|
|
Division between Western and Eastern Churches • Authority of the Pope eventually accepted in the West • Authority of the Patriarch accepted in the East • Practices such as celibacy eventually accepted in the West
|
|
Why did the Byzantine Empire have so much influence on religion, culture, and trade in Russia and Eastern Europe?
|
|
Influence of Byzantine culture on Eastern Europe and Russia • Trade routes between Black Sea and Baltic Sea • Adoption of Orthodox Christianity by Russia and much of Eastern Europe • Adoption of Greek alphabet for the Slavic languages by St. Cyril (Cyrillic alphabet) • Church architecture and religious art-Use of Icons and Domes
|
| This man was the founder of Islam |
| Muhammad |
| Where did Islam originate? |
In the cites of Mecca and Medina on the Arabian Peninsula. 
|
| Where did Islam spread? |
|
Across Asia and Africa into Spain. |
| What are the beliefs, traditions, and customs of Islam? |
|
Beliefs, traditions, and customs of Islam · Monotheism: Allah (Arabic word for God) · Qur’an (Koran): The word of God · Five Pillars of Islam Acceptance of Judeo-Christian prophets, including Moses and Jesus
|
These are the: |
| Five pillars of Islam |
|
This building is the focal point of the Hajj.
|
| Kaaba |
|
How did geography influence the rapid expansion of territory under Muslim rule?
|
|
Geographic influences on the origin and spread of Islam · Diffusion along trade routes from Mecca and Medina · Expansion despite great distances, desert environments, and mountain barriers · Spread into the Fertile Crescent, Iran, and Central Asia facilitated by weak Byzantine and Persian empires
|
|
How did political and cultural geography facilitate trade and cultural activity in the early Islamic lands? |
|
Geographic influences on economic, social, and political development · Political unity of the first Muslim empire was short-lived. · Arabic language spread with Islam and facilitated trade across Islamic lands. Slavery was not based on race.
|
|
What were some major historical turning points that marked the spread and influence of Islamic civilization? |
|
Historical turning points · Death of Ali: Sunni-Shi’a division · Muslim conquests of Jerusalem and Damascus · Islamic capital moved to Baghdad-Abbasid Dynasty · Muslim defeat at the Battle of Tours by the Franks in 732 Fall of Baghdad to the Mongols
|
| Muslims who believe the Caliph does not need to be a direct relative of Muhammad. |
| Sunni |
| Muslims who believe that the Caliph should be a direct descendant of Muhammad. |
| Shia (Shiite) |
|
How did Islamic civilization preserve and extend ancient Greek, Persian, and Indian learning?
|
| Muslim Universities studied the works of the Greeks, Persians, and India. They copied and wrote commentaries on works from these cultures. |
|
What is the name of this structure? |
| Dome of the Rock |
| Muslim scholars translated Greek, Persian, and Indian works into this language. |
| Arabic. |
|
Many mosques and Muslim buildings are decorated with these types of images.
|
| Mosaic |
|
What were some contributions of Islamic civilization? |
|
Scientific contributions and achievements · Arabic numerals (adapted from India, including zero) · Algebra · Medicine Expansion of geographic knowledge
|
| What influences formed the foundation of Medieval society? |
|
Foundations of early medieval society · Classical heritage of Rome · Christian beliefs · Customs of Germanic tribes
|
|
How and why did the Church grow in importance during the Middle Ages? |
|
Influence of the Roman Catholic Church · Secular authority declined, while Church authority grew. · Monasteries preserved Greco-Roman cultural achievements. · Missionaries carried Christianity and Latin alphabet to Germanic tribes. · The Pope anointed Charlemagne Emperor in 800 a.d. (c.e.) Parish priests served religious and social needs of the people.
|
| Why did feudalism develop in Europe? |
| Invasions in Europe shattered the Roman protection, people needed protection. |
| What was a fief? |
| The land given to a vassal by a lord. |
| In feudalism a lord gave land to a _____. |
| Vassal |
| In the middle ages, these were peasants who were bound to the land. |
| Serfs |
| In feudalism, a vassal owed certain feudal obligations to his lord these included: |
|
Rent Military service Loyalty |
|
How did the medieval manor function as a social and economic system? |
|
Manorial system during the Middle Ages
|
Charlemagne was from this tribe.
|
| Franks |
| Why was Pope Leo III's crowning of Charlemagne significant? |
It linked both religious and political power. 
|
| What areas were conquered by Charlemagne? |
|
Most of Western Europe.
|
|
How did Charlemagne revive the idea of the Roman Empire? |
|
Age of Charlemagne · Franks emerged as a force in Western Europe. · The Pope crowned the Emperor. · Power of the Church was established in political life. · Roman culture was reinterpreted. · Most of Western Europe was included in the new empire. Churches, roads, and schools were built to unite the empire.
|
| What area was settled by the Angles and Saxons? |
|
· Angles and Saxons migrated from continental Europe to England.
|
| Where did the Magyars settle? |
|
Magyars migrated from Central Asia to Hungary.
|
|
Where were the Vikings from?
|
| Scandinavia |
| What Russian culture was established by the Vikings |
| Kievan Rus |
|
How did invasions by the Angles, Saxons, Magyars, and Vikings influence the development of Europe? |
|
Influence of the Angles, Saxons, Magyars, and Vikings · Manors with castles provided protection from invaders, reinforcing the feudal system. Invasions disrupted trade, towns declined, and the feudal system was strengthened.
|
| What were the major trade routes of the Eastern Hemisphere from 1000 to 1500 CE. |
|
Major trade patterns of the Eastern Hemisphere from 1000 to 1500 a.d. (c.e.) Silk Routes across Asia to the Mediterranean basin
|
| What goods came from West Africa? |
| Gold |
| What goods came from the area around the Indian Ocean. |
| Spices |
| What regions produced textiles? |
|
India, China, the Middle East, and later Europe |
| What product was manufactured by China and Persia? |
| Porcelain |
| What product was produced by the Baltic? |
Amber
|
| From what areas did the Europeans gain paper-making technology? |
|
· Paper came from China through the Muslim world to Byzantium and Western Europe
|
| What new crops did the Europeans gain from India? |
| Sugar |
| What agricultural technology did the Europeans learn from the Middle East. |
| Watermills and Windmills |
| What navigational innovations did the Europeans learn from China and India? |
|
Navigation: Compass from China, lateen sail from Indian Ocean region |
| How did various religions spread across the Eastern Hemisphere? |
|
Ideas · Spread of religions across the hemisphere – Buddhism from China to Korea and Japan – Hinduism and Buddhism from India to Southeast Asia – Islam into West Africa, Central and Southeast Asia
|
| What culture gave paper to the west? |
|
Printing and paper money came from China |
|
How has Japan’s geography influenced its development?
|
|
Location and place · Mountainous Japanese archipelago (four main islands) · Sea of Japan or East Sea between Japan and Asian mainland · Proximity to China and Korea
|
|
How did Chinese culture influence Japan?
|
|
Influence of Chinese culture
|
|
Why were Shinto and Buddhism important to the development of Japanese culture?
|
|
Shinto · Ethnic religion unique to Japan · Importance of natural features, forces of nature, and ancestors · State religion; worship of the emperor Coexistence with Buddhism
|
 Describe the Medieval civilization of Axum. Describe the Medieval civilization of Axum.
|
|
Axum · Location relative to the Ethiopian · Christian kingdom
|
Describe the Medieval civilization of Zimbabwe.
|
|
Zimbabwe · Location relative to the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers and the Indian Ocean coast. Was between the Zambezi and Limpopo river. · City of “Great Zimbabwe” as capital of a prosperous empire
|
| The West African civilizations of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai were all along this river. |
| Niger |
| These two products were vital to the trans Saharan trade. |
| gold and salt |
| This city was the capital of Mali and was a great center of learning. |
|
Timbuktu
|
| The animistic African religions came into conflict with this religion when it swept across Africa. |
| Islam |
|
What were some characteristics of the Mayan civilization?
|
|
Mayan civilization · Located in the Mexican and Central American rain forests · Represented by Chichén Itzá · Groups of city-states ruled by kings · Economy based on agriculture and trade · Polytheistic religion: Pyramids
|
|
What were some features of the Aztec civilization?
|
|
Aztec civilization · Located in arid valley in central Mexico · Represented by Tenochtitlan · Ruled by an emperor · Economy based on agriculture and tribute from conquered peoples Polytheistic religion: Pyramids, rituals
|
What were some features of the Incan civilization?
|
|
Incan civilization · Located in the Andes Mountains of South America · Represented by Machu Picchu · Ruled by an emperor · Economy based on high-altitude agriculture · Polytheistic religion · Road system
|
|
What were the achievements of Mayan, Aztec, and Incan civilizations |
|
· Calendars · Mathematics Writing and other record-keeping systems
|
|
This man was leader of the Norman Conquest, united most of England |
|
William of Normanday/William the Conqueror
|
| This king established common law in England. |
| Henry II |
| This English king signed the Magna Carta, limiting the king's power. |
| King John |
| This long war between England and France helped to define both countries as distinct nations. |
|
The Hundred Years War.
|
| King Edward I called this as an advisory body in England, but it eventually came to control finances. |
| Parliament. |
| This man established the French throne in Paris, and his dynasty gradually expanded their control over most of France. |
| Hugh Capet |
| This woman was a unifying factor for the French in the 100 years war. |
Joan of Arc
|
|
This Spanish King and Queen unified the country and expelled Jews and Moors.
|
|
Ferdinand and Isabella The Reconqista |
|
Spanish Empire in the Western Hemisphere expanded under:
|
| Charles V |
|
This man threw off the rule of the Mongols, centralized power in Moscow, and expanded the Russian nation.
|
|
Ivan III (Ivan the Great)
|
| The Russian imperial leader was known as the: |
|
Tsar
|
| This branch of Christianity influenced Russian unification. |
|
The Orthodox Church
|
| What were some of the key events of the crusades? |
|
Key events of the Crusades · Pope Urban’s speech · The capture of Jerusalem · Founding of Crusader states · Loss of Jerusalem to Saladin · Sack of Constantinople by western Crusaders
|
| What were some of the effects of the Crusades? |
|
Effects of the Crusades · Weakened the Pope and nobles; strengthened monarchs · Stimulated trade throughout the Mediterranean area and the Middle East · Left a legacy of bitterness among Christians, Jews, and Muslims · Weakened the Byzantine Empire
|
|
What were the effects of the Mongol invasions?
|
|
Mongol armies · Invaded Russia, China, and Muslim states in Southwest Asia, destroying cities and countryside · Created an empire
|
|
What were the effects of the Ottoman invasions of Europe? |
|
Constantinople · Fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453, ending the Byzantine Empire Became capital of the Ottoman Empire
|
|
How did the Black Death (Bubonic plague) alter economic and social institutions in much of Asia and then in Europe?
|
|
Impact of the Black Death (Bubonic plague) · Decline in population · Scarcity of labor · Towns freed from feudal obligations · Decline of Church influence Disruption of trade
|
|
How did European scholars begin to interpret and value ancient learning?
|
|
Church scholars · Were among the very few who could read and write · Worked in monasteries · Translated Greek and Arabic works into Latin · Made new knowledge in philosophy, medicine, and science available in Europe Laid the foundations for the rise of universities in Europe
|
|
How did the Crusades stimulate trade between Europe and the Muslim Empire?
|
|
Economic effects of the Crusades · Increased demand for Middle Eastern products · Stimulated production of goods to trade in Middle Eastern markets · Encouraged the use of credit and banking
|
|
What were the economic foundations of the Italian Renaissance? |
|
Important economic concepts · Church rule against usury and the banks’ practice of charging interest helped to secularize northern Italy. · Letters of credit served to expand the supply of money and expedite trade. New accounting and bookkeeping practices (use of Arabic numerals) were introduced.
|
|
How did northern Italian cities benefit from their geographic location?
How did Italian city-states achieve importance and develop politically?
|
|
Florence, Venice, and Genoa · Had access to trade routes connecting Europe with Middle Eastern markets · Served as trading centers for the distribution of goods to northern Europe · Were initially independent city-states governed as republics
|
|
What were Machiavelli’s ideas about power?
|
|
Machiavelli’s The Prince · An early modern treatise on government · Supports absolute power of the ruler · Maintains that the end justifies the means Advises that one should not only do good if possible, but do evil when necessary
|
|
How did the arts and literature of the Renaissance differ from those of the Middle Ages?
|
|
Medieval art and literature focused on the Church and salvation, while Renaissance art and literature focused on individuals and worldly matters, along with Christianity.
|
|
Who painted this work?
|
| Da Vinci-The Mona Lisa |
|
Who painted this work?
|
|
Michelangelo The Sistine Chapel The Creation of Man |
|
Who painted this work?
|
| Da Vinci |
 Who sculpted this work? Who sculpted this work?
|
|
Michelangelo
The David |
| What did Petrarch contribute to the Renaissance. |
|
Humanist scholarship Researched Greek and Roman Writings Wrote, Sonnets to Laura in the vernacular.
|
|
How did knowledge of the classical Greeks and Romans foster humanism in the Italian Renaissance? |
|
Humanism · Celebrated the individual · Stimulated the study of classical Greek and Roman literature and culture -Supported by wealthy patrons
|
|
How did ideas of the Italian Renaissance change as they were adopted in northern Europe?
|
|
Northern Renaissance · Growing wealth in Northern Europe supported Renaissance ideas. · Northern Renaissance thinkers merged humanist ideas with Christianity.
|
 How did this invention change life in the Renaissance? How did this invention change life in the Renaissance?
|
|
The Gutenberg printing press: · The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (e.g., Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas.
|
 How did Erasmus influence the Renaissance? How did Erasmus influence the Renaissance?
|
|
· Erasmus: The Praise of Folly (1511) He criticized the Church through the use of satire.
|
|
Who was Sir Thomas More?
|
| He was an English humanist. He wrote Utopia which described an ideal world. |

























 the Parthenon.
the Parthenon.
























 Highlands and the Nile River
Highlands and the Nile River.JPG)














