| Lithospheric Plates |
| Regions of Earth's crust and upper mantle that are fractured into plates that move across a deeper plasticine mantle. |
| divergent plate boundaries |
| two plates move apart from each other and the space that this creates is filled with new crustal material sourced from moltenmagma that forms below. |
| convergent plate boundaries |
|
two (or more) tectonic plates or fragments oflithosphere move toward one another and collide. |
| Oceanic-continental convergent plate boundaries |
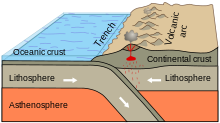
|
| Continental-continental convergent plate boundaries |

|
| Oceanic-oceanic convergent plate boundaries |

|
| transform-fault plate boundary |
|
ex: san andres fault |
| Things Proving Plate Tectonics |
|
|
Oldest Oceanic Crust? Oldest Continental crust? |
|
oceanic ~ 200 Million Years continental ~ 3.8 Billion Years |
| Mineral |
| naturally occuring compound or chemical element made of atoms arranged in an orderly, repetative pattern |
| Luster |
|
appearance of minerals when light is relfected from its surface
metallic vs. non-metallic |
| Hardness |
| resistance of a smooth surface to abraison or scratching |
| Mohs Hardness Scale |

|
| cleavage |
| break along flat planes |
| fractures |
|
breakage that is not on a flat surface. Two main kinds of fracture are conchoidal (shell shaped, as in quartz) and uneven |
| Crystal |
|
a solid, homogenous, orderly array of atoms
|
|
|
|
Potassium Feldspar luster: non-metallic hardness: 6 Streak: White Cleavage: 2 @ 90 deg other properties: no striations |

|
|
Gypsum luster: non-metallic hardness: 2 Streak: White Cleavage: 3 not @ 90 deg other properties: striations |
|
|
|
Galena luster: metallic hardness: 2.5 Streak: black Cleavage: 3 @ 90 deg
|

|
|
Biotite luster: non-metallic hardness: 1 Streak: blackish Cleavage: 1 other properties: flakey |

|
|
Sulfur luster: non-metallic hardness: 1.5-2.5 Streak: yellowish Cleavage: 0 other properties: smell |

|
|
Pyrite luster: metallic hardness: 6-7 Streak: black Cleavage: 3 @ 90 deg
|

|
|
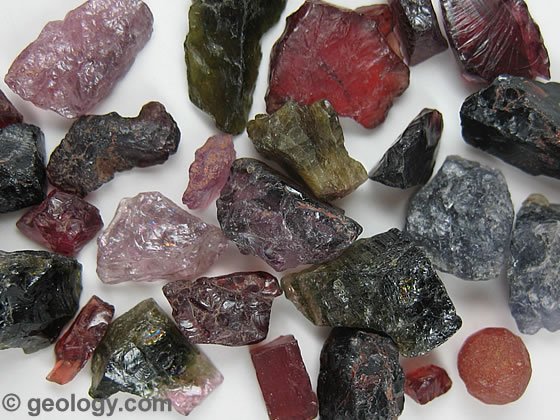
Garnet luster: non-metallic hardness: 6-7 Streak: colorless Cleavage: 0
|

|
|
Chalcopyrite
luster: metallic
hardness: 3.5-4
Streak: greenish black
Cleavage: 0
other properties: softer than pyrite
|

|
|
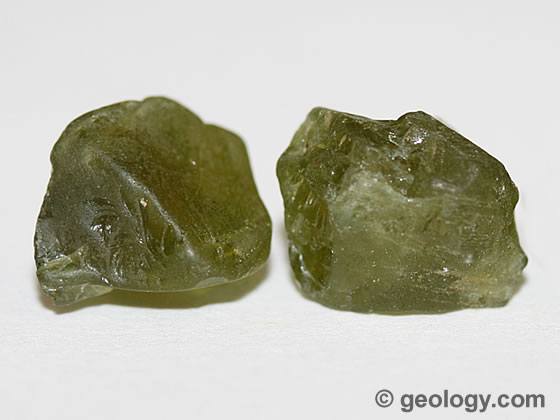
Olivine luster: non-metallic hardness: 6-7 Streak: White Cleavage: 0 other properties: glassy luster, color |

|
|
Muscovite luster: non-metallic hardness: 1-2 Streak: White Cleavage: 1 other properties: transparent
|

|
|
Corundum luster: non-metallic hardness: 7-8 Streak: White Cleavage: 3 not @ 90 deg
|

|
|
Halite luster: non-metallic hardness: 2-3.5 Streak: White Cleavage: 3 @ 90 deg other properties: tastes salty |

|
|
Hematite luster: metallic hardness: 5.5-7 Streak: redish grey Cleavage: 0
|

|
|
kaolinite luster: non-metallic hardness: < 2 Streak: White Cleavage: 0
|

|
|
Quartz luster: non-metallic hardness: 7 Streak: White Cleavage: 3 not @ 90 deg other properties: multi colored, pyramid heads |

|
|
Calcite luster: non-metallic hardness: 2-3.5 Streak: colorless Cleavage: 3 not @ 90 deg other properties: reacts w/ HCl |

|
|
Magnetite luster: metallic hardness: 5.5 Streak: black Cleavage: 0 other properties: magnetic |

|
|
Plagiocase luster: non-metallic hardness: 6-7 Streak: colorless Cleavage: 2 not @ 90 deg
|

|
|
Flourite luster: non-metallic hardness: 4 Streak: white Cleavage: 4 not @ 90 deg other properties: purple, green |
|
|
|
Pyroxene luster: non-metallic hardness: 7 Streak: white Cleavage: 2 not @ 90 deg
|

|
|
Hornblende luster: non-metallic hardness: 5-6 Streak: gray/ greenish black Cleavage: 0
|
| Mafic |
|
dark in color form an mid-ocean ridges hot spots |
| Felsic |
|
light in color form at subduction zones continental material needed |
| Intermediate |
|
mix of mafic and felsic form at subduction zones rare -> mid ocean ridges |
| Intrusive Rocks |
| igneous rocks that cool beneath the surface |
| Extrusive Rocks |
| igneous rocks that cool on the surface |
| Pegmatitic |
|
igneous rocks with crystals > 3cm high H2O slow cooling |
| Vesicular |
|
igneous rock w/ holes gas rich lava <60% vesicals
|
| Scoriacous |
|
igneous rock > 60% vesicals |
| prophoryitic |
|
igneous rock w/ 3 crystal sizes slow cooling ----> fals cooling "chocloate chip cookies" |
| glassy |
|
igneous rocks instant cooling |

|
|
Scoria texture: vesicular mineral composition: mafic other properties: black/ red color orgin: cinder cone |

|
|
Basalt texture: aphanitic mineral composition: mafic other properties: almost black in color orgin: Mid-ocean ridge/hot spots |

|
|
Pumice texture: glassy w/ several small vesicles mineral composition: felsic other properties: light grey in color orgin: froth of volcanic glass |

|
|
Diorite texture: course grained (phaneritic) mineral composition: intermediate other properties: black/white color orgin: intrusive |
|
|
|
Granite texture: phaneritic mineral composition: felsic other properties: black/grey/pinkish in color orgin: slow-cooling |

|
|
Obsidian texture: glassy mineral composition: intermediate other properties: black orgin: instant cooling |
|
|
|
Gabbro texture: phaneritic mineral composition: mafic other properties: mostly dark colored orgin: slow-cooling |
|
|
|
Rhyolite Tuff texture: pyroclastic mineral composition: felsic other properties: sandy color orgin: 2-step cooling
|
|
|
|
Vesicular Basalt texture: scoriacous mineral composition: mafic other properties: black orgin: lava flow or cinder cone |

|
|
Porphyritic Granite texture: course grained (prophyctic) mineral composition: felsic other properties: pink/grey orgin: slow-cooling/intrusive
|

|
|
Rhyolite texture: fine grained (aphanitic) mineral composition: felsic other properties: tan/pink orgin: slow-cooling/intrusive |
|
|
|
Andesite/Porphyry texture: porphoritic mineral composition: intermediate other properties: gray w/ black crystals orgin: 2-step cooling |
| steps to form sedimentary rocks |
|
| weathering |
|
physical ---> ex. freeze thaw chemical----> ex. H2O disolve existing minerals |
| erosion/transportation |
|
| compaction & cementation |
|
| 3 basic sediment reactions |
|
| Clastic Sediment Reaction |
gravel > 2mm sand 2mm - 0.063mm |
| Biogenic Sediment Reactions |
|
| Chemical Sediment Reaction |
|
| graded bedding |
|
sedimentary deposition fine medium largest |
| Ripple Marks |
|
sedimentary structure symetrical vs. asymetrical |
| cross bedding |
|
sedimentary structure caused by current (diagonal bedding) |
| Horizontal Bedding |
|
sedimentary structure no current needed (horiz bedding) |
| Mudcracks |
|
sedimentary structure mracks on top of rock, used to be mud |

|
|
Arkose texture: Clastic mineral composition: Quartz sorting/roundness: well-sorted & rounded depositional conditions: alluvial fan |

|
|
Rock salt texture: crystalline mineral composition: halite depositional conditions: euforite basin |
|
|
|
Coal texture: bioclastic mineral composition: carbon fossils/ condition: leaves depositional conditions: compacted vegitation |

|
|
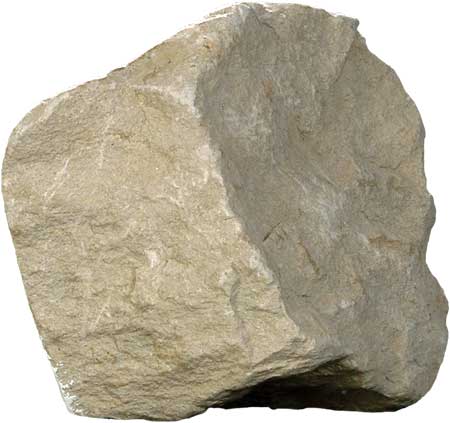
Clastic Limestone texture: bioclastic mineral composition: calcite fossils/ condition: shels clams, broken depositional conditions: beach enviroment |

|
|
Mudstone texture: Clastic mineral composition: clay sorting/roundness: rounded, well-sorted depositional conditions: deep ocean |

|
|
Breccia texture: clastic mineral composition: Calcite sorting/roundness: poorly sorted depositional conditions: glacier |
|
|
|
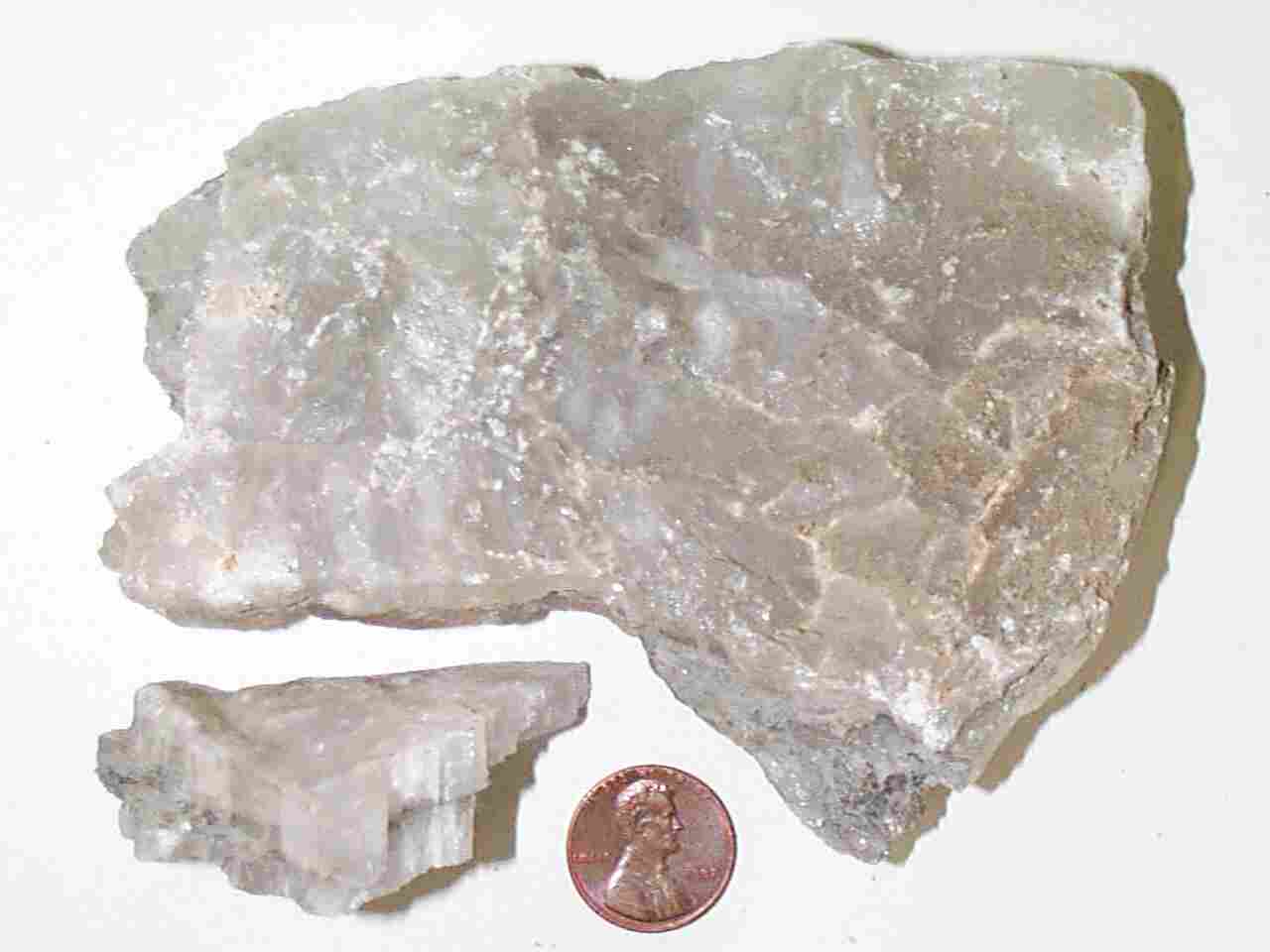
Coquina texture: bioclastic mineral composition: calcite fossils/ condition: clams, broken up depositional conditions: beach enviroment/reef |

|
|
Rock Gypsum texture: crystalline mineral composition: gypsum depositional conditions: evaporite basin
|
|
|
|
Chert texture: crystalline mineral composition: quartz sorting/roundness: angular depositional conditions: deep ocean |
|
|
|
Conglomerate texture: clastic mineral composition: quartz and k-spar sorting/roundness: well sorted, rounded depositional conditions: riverbed |
|
|
|
Claystone texture: bioclastic mineral composition: calcite sorting/roundness: rounded, well sorted fossils/ condition: micro fossils, whole depositional conditions: deep ocean |
|
|
|
Shale texture: clastic mineral composition: clay minerals sorting/roundness: round, well sorted depositional conditions: deep ocean |
|
|
|
Calcite texture: crystalline mineral composition: calcite depositional conditions: marine shelf |
| protolyth |
|
parent rock "what did it used to be?"
|
| Regional |
|
large events heat, pressure, fluid foliation - parallel alignment of minerals (only in regional settings) |
| contact |
|
localized - heat & fluids types:
|
| facies |
| assemblage of minerals that reflects the temperature pressure of formation and can relate to a tectonic setting |
|
|
|
Slate Foliation: foliated Texture: fine grained composition: slaty cleavage, "ping" sound when dropped grade: Low uses: roofing protolith: shale |
|
|
|
Gneiss Foliation: foliated Texture: medium grained, crystaline composition: light & dark, layers, banded grade: high uses: monuments, counters protolith: granite, shale, mudstone
|
|
|
|
Schist Foliation: foliated Texture: crystaline composition: crystals apearent, scaley look grade: medium-high uses: garnet protolith: shale, mudstone |

|
|
Phyllite Foliation: folliated Texture: phylitic composition: silky, shiny luster grade: low- medium uses: tall decrotive statues protolith: shale |

|
|
Marble Foliation: non foliated Texture: crystalline composition: chiefly calcite, reacts w/ HCl grade: low-medium uses: indoor decorative protolith: limestone |
|
|
|
Quartzite Foliation: non foliated Texture: crystalline composition: chiefly quartz, scratches glass grade: medium- high uses: building stone protolith: quartz sandstone |
|
|
|
Anthracite Coal Foliation: non foliated Texture: crystalline composition: shiny, dark, conchoidal fracture grade: low uses: fuel/energy protolith: coal |
