|
What is it Prophase
|
|
1st phase of Mitosis -spindle fibers form bridge over nucleus |
|
what is Metaphase
|
|
2nd phase of Mitosis when chromosomes line up across equator of cell
|
|
What is Anaphase
|
|
What is The 3rd phase of Mitosis when -chromosomes split and spindles retract to opposite sides of the cell pulling the chromosomes along with them |
|
What is Telophase
|
|
What is the 4th and Final phase of Mitosis when-nuclear envelope forms around the 2 new nuclei |
|
What is the Nucleolus
|
| What is the – oval structure inside the nucleus that makes the ribosomes |
|
WHat is the Nuclear envelope
|
|
WHat is - the skin around the nucleus |
|
What are Ribosomes
|
| What are the organelles that – produce proteins (and look like tiny dots) |
|
What is the Cell membrane
|
|
WHat us - the outside skin of the cell separating the cytoplasm from the environment around the cell called |
|
What is the Cytoplasm
|
|
What is the - jell-like fluid that fills the cell, in which most of the organelles live called |
|
What are the Mitochondria
|
|
What are the organelles that produce energy for cell activity called |
|
What is the Endoplasmic reticulum smooth and rough!
|
|
What is the- network of passageways throughout the cell called |
|
What is the Nucleus
|
|
What is the Brain of the cell, that directs actions of the cell |
|
What are Lysosomes
|
|
What are the – cell's clean up crew |
|
WHAT ARE Vacuoles
|
|
What are the –organelles for the storage of cell water,waste, & food ( plants have one big one full of water) |
|
What are Gogli bodies
|
|
WHAT ARE - transporters of THE cell CALLED - pancakes |
|
What are Organelles
|
|
what are - cell organs called |
|
What is a Purebred
|
|
What is - The offspring of many generations that have the same trait. Ex: short pea plants always come from short parent plants |
|
WHAT is Hybrid
|
| What is- The offspring of genetically dissimilar parents, especially the offspring produced by breeding plants or animals of different varieties, species, or races. Example: offspring inherits 1 allele for tallness from pure bred tall plants, and 1 allele from a purebred short plant for shortness. The off spring will be a ____ and it will be tall because tallness is dominant. |
|
WHAT IS A Recessive Allele
|
| WHAT is-the allele trait that is always hidden when the dominant trait is around. the dominant allele always wins when its around - IF a dominant gene for tallness from one parent and a recessive gene for shortness from the other parent pair up, tallness will be inherited because its dominant. You need two shortness genes to pair up to inherit shortness. |
|
What is Dominant allele
|
|
WHAT IS - the GENE whose trait always shows up in the offspring |
|
What is a Trait
|
|
What is - each different form of a characteristic such as hair color, height, called
|
|
What is F2 Generation
|
|
What is the The 2nd Filial Generation The offspring resulting from a cross or mating of F1 Generation plants - the grandchildren of a parent plant |
|
F1 Generation
|
|
- The 1st Filial Generation, resulting from a cross between 2 breeding plants.
Homozygous for the trait of interest. |
|
What is the Filial Generation
|
|
What are - children of the parent organism called ex: You cross two plants and get a baby plant. Its the ________ _________. |
|
What is a Dominant Trait
|
|
What is - A trait that is expressed over another trait. Example: So if the brown hair gene is a ______ _______ over blonde hair and you have a blonde and a brown hair gene from each of our parents, you’ll have brown hair. |
|
What are Alleles
|
|
what are - The different forms of a gene.
For example- You inherit one ____ from each parent for a trait, for example - tallness. How tall depends on the ____s. |
|
What is Heredity
|
|
What is the passing of physical characteristics from parent to offspring called |
|
What is Genetics
|
|
What is the study of heredity (of genes) called |
|
What is a Gene
|
|
- a segment of DNA on a chromosome, that holds the information for a specific trait - the brown eyes gene or the freckles gene |
|
what is DNA replication
|
|
-two sides of DNA unzip! – 4 free floating nitrogen bases pair up with the 4 nitrogen bases inside the unzipped DNA. After the new bases attach, new DNA molecules are formed |
|
what is DNA
|
|
-carrier of genetic information- - A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell- (DNA is carried in the chromosomes) (De-ox-y-ri-bo - nu-cle-ic a-cid)
|
|
WHat is Cytokinesis
|
|
final stage of the cell cycle, -completes cell division cycle- Cytoplasm pinches middle of the cell - cell divides, then organelles are distributed to each new daughter cell |
|
What is Mitosis
|
|
what is - the 2nd stage of the Cell Cycle - when Cell Division occurs (= parent cell divides into 2 daughter cells) There are 4 phases of Mitosis ( P.Mat) Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telephase) |
|
What is Interphase
|
|
- 1st stage in the cell cycle cell grows getting ready to divide & replicate its DNA during Mitosis |
|
What is the Cell Cycle
|
|
What is The orderly set of events of a cells growth and division (AKA-the life cycle of a cell-which has 3 parts: Interphase, Mitosis and Cytokinesis) called |
|
What is Replication
|
|
What is - to make a duplicate or twin of one's self called |
|
What is a Chromosome
|
|
- What are-Many genes joined together- During prophase, Chromatin condenses and the DNA replicates to form two rods called chromatid, exact copies of each other. This double rod of chromatids is called a__________ |
|
WHAT IS Meiosis (mi-o-sis)
|
|
WHAT IS THE formation of sex cells (sperm and egg) - the number of chromosomes is halved -It has 4 phases, like Mitosis, but it’s phases repeat, - replicate 2 times, so there’s Prophase 2 and metaphase 2 and so on
|
|
WHAT IS A Cell
|
|
WHAT IS THE basic unit of structure of all living things called |
|
|
|
WHAT DOES Telophase look like |

|
|
WHat does metaphase look like |
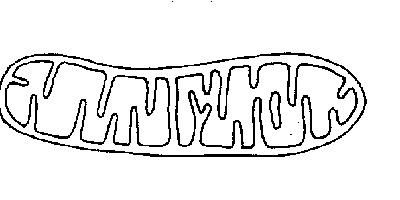
|
|
What does mitochondria look like (They make energy for the cell) |
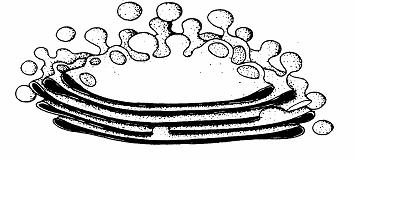
|
|
Gogli body pancake like makes proteins transporter of the cell
|
|
Which organelle is the Gogli body Ribosome Centriole Endoplasmic reticulum- smooth and rough Nucleus Nucleolus Lysosome Mitochondria Cytoplasm
|
|
cytoplasm = cytosol Ignore the Pinocytotic Vesicle |
|
Two important differences between processes of mitosis and meiosis are: |
|
|
|
Where are the chromosomes in a cell? |
|
in the nucleus the brains of the cell |
|
What are the 2 types of cell division? |
|
mitosis and meiosis |
|
adenine |
|
One of the four nitrogen bases in DNA |
|
What are centrioles |
|
cylinder shaped organelles -that pair up, -pairs go to either side of the cell then -shoot out spindle fibers -during prophase |
|
What are chloroplasts |
|
Disc shaped organelles found in plant cells (not animal cells) that help the plant turn sunlight into food |
|
A nucleic acid composed of two strands with bars in between like a ladder twisted into a spiral forming a double helix shape and carries the genetic information of the cell |
|
What is DNA What do the letters stand for? |
|
What is guanine |
|
One of the 4 nitrogen bases in DNA |
|
The period between cell divisions (before Mitosis) when cell grows in preparation for the next division (3rd part of cell cycle) |
|
What is interphase |
|
Organelles that contain digestive juices that break down food, and cell waste the clean up crew of the cell |
|
What are lysosomes |
|
Cell division in which the chromosomes replicate like in Mitosis but is followed by 2 nuclear divisions (nucleus of cell divides 2 times ,not one time like in Mitosis) resulting in 4 daughter SEX cells (gametes) |
|
What is meiosis |
|
The stage of cell division (in mitosis or meiosis) when chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell |
|
What is metaphase |
|
A network of thread like fibers formed during prophase that attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes and help draw the chromosomes apart during anaphase |
|
What are spindles |
|
The unexpected change in a gene, that makes a different form of that gene that can be inherited by future generations, (caused by an accidental change in the DNA)
|
|
What is mutation |
|
Name of the Cell parts that carry out individual functions of the cell like the organs inside our body's do |
|
What are organelles |
|
What are chloroplasts and cell wall |
| What are two things a plant cell has that a animal cell doesn't have? |
|
Process by which DNA is duplicated before cell division |
|
What is replication |
|
WHat DO THEY CALL - cells breathing |
|
WHAT IS "cellular respiration" |
|
Organelles - look like tiny dots freely floating around inside the cell and -attach to the endoplasmic reticulum(ER) they help make proteins |
|
What are Ribosomes |
|
The final stage of mitosis When the chromosomes migrate to opposite poles, a new nuclear envelope forms, and the chromosomes uncoil |
|
What is Telophase |
|
What do you call the - (foursomes) - 2 chromosomes from mom and dad (2 overlapping X's, that are made up of 4 lines - the chromatids) that occur during Meiosis? XX |
|
WHat are Tetrads (tedrad means 4 things together.) Count the rods that make up the two X's !) |
|
what is Thymine |
|
One of the 4 nitrogen bases in DNA that begins with a T |
|
What are the Fluid-filled spaces or capsules in plant and animal cells that remove waste products and store ingested food. There's usually one big one, full of water, in plants |
|
WHat are vacuoles |
|
Why do sex cells created in Meiosis, have only half as many chromosomes as a cell needs ? |
|
Because they are going to join up with other sex cells from the other parent to make offspring (baby) cells. -Then it will add its half to the other parent's half to make one complete cell |

|
|
The spindles are pulling the chromosomes towards opposite poles of the cell where they will become part of 2 new nuclei for 2 new daughter cells- in Mitosis and Meiosis - it will happen 2 times in Meiosis. It is called just plane anaphase in Mitosis. |

|
|
YOu can tell this is _________ , of MEIOSIS because there are 2 cells now not just one like there is in Mitosis, whose spindles are pulling the chromosomes towards opposite poles , getting ready for the second split in Telephase, so that there will be 4 daughter cells |

|
|
THESE ARE 2 PICTURES of 1 cell picture 1- BEGINNING OF _______ picture 2 - THE END OF ________ YOU CAN TELL BECAUSE: picture 1-YOU CAN'T SEE ANY CHROMOSOMES picture 2- now THE CHROMATIN HAVE Condensed/Fattened up INTO CHROMOSOMES; and Nuclear Wall is breaking up, losing its shape. What you cant see in the photo = are the CENTROMERES going to opposite poles of the cell while spindle fibers make a bridge between them. |

|
|
In this phase of Mitosis & Meiosis, the chromosomes(in red) have all split and have been pulled by the spindle fibers to opposite poles of the cell. 2 new nuclei have formed and the cell is ready for the last phase - when it will elongate before Cytosis |

|
|
In this phase of Mitosis and Meiosis, the chromosomes are all lined up at the equator of the cell. The spindle fibers are there too, attached to the chromosomes. they look like faint squiggly lines ready for the next phase when they will pulled apart chromosomes to either pole of the cell |
|
WHat is a Helix |
|
what is An object in the shape of a corkscrew, a spiral staircase or a spiral called |
|
Adenine & thymine AT pair up Guanine & Cytosine G,C pair up |
|
The 4 Nitrogen bases that make up the rungs on the spiral ladder of DNA & that unzip when DNA replicates |
|
What is shaped like a Double Helix |
|
What is the Shape of DNA |
|
|
|
What does "ER" (Endoplasmic Reticulum) network of passageways in the cell Look like? what does it look like? |
|
Each ________ consists of two identical "sister" chromatids attached by a centromere. |
|
A Chromosome is made up of two ________s attached by a ___________. |
|
WHAT IS PMat, or |
|
What are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telephase |


